How to MCP Connect to GitHub
Step-by-step guide to connecting the GitHub MCP server to MCP clients like Claude Desktop and MCP Connect. Learn to configure GitHub authentication, manage repositories with AI, and develop with visual protocol inspection and real-time debugging.
Learn how to integrate GitHub's powerful platform with MCP Connect for seamless AI-powered repository management
Keen to learn more about MCP from in-person experts? Check out our upcoming MCP Bangkok (16th October 2025) and MCP Singapore (23rd October 2025) meetups.
What is the GitHub MCP Server?
The GitHub MCP Server connects AI tools directly to GitHub's platform, enabling AI agents, assistants, and chatbots to interact with repositories, code files, issues, pull requests, and workflows through natural language interactions.
Key Benefits:
- Repository Management: Browse code, search files, analyze commits, and understand project structure
- Issue & PR Automation: Create, update, and manage issues and pull requests with AI assistance
- CI/CD Intelligence: Monitor GitHub Actions workflows, analyze build failures, and manage releases
- Code Analysis: Review security findings, Dependabot alerts, and code patterns
- Team Collaboration: Access discussions, manage notifications, and streamline team processes
Understanding Model Context Protocol (MCP)
Model Context Protocol (MCP) is an open standard created by Anthropic that enables seamless integration between AI applications and external data sources. Think of it as a universal adapter that allows AI models like Claude to securely access and interact with your repositories, APIs, and tools.
Why MCP Matters:
- Standardized Integration: One protocol for all your data sources
- Secure Access: Controlled, auditable data access for AI models
- Real-time Context: AI models work with live, up-to-date information
- Tool Capabilities: Extend AI models with custom functionality
With MCP, your AI applications can interact with GitHub repositories, manage issues and PRs, analyze code, and more—all through a consistent, secure interface.
Prerequisites
Before getting started, you'll need:
- Docker Desktop installed and running
- A GitHub Personal Access Token (we'll create this together)
- Node.js installed (for running the MCP gateway)
Creating Your GitHub Personal Access Token
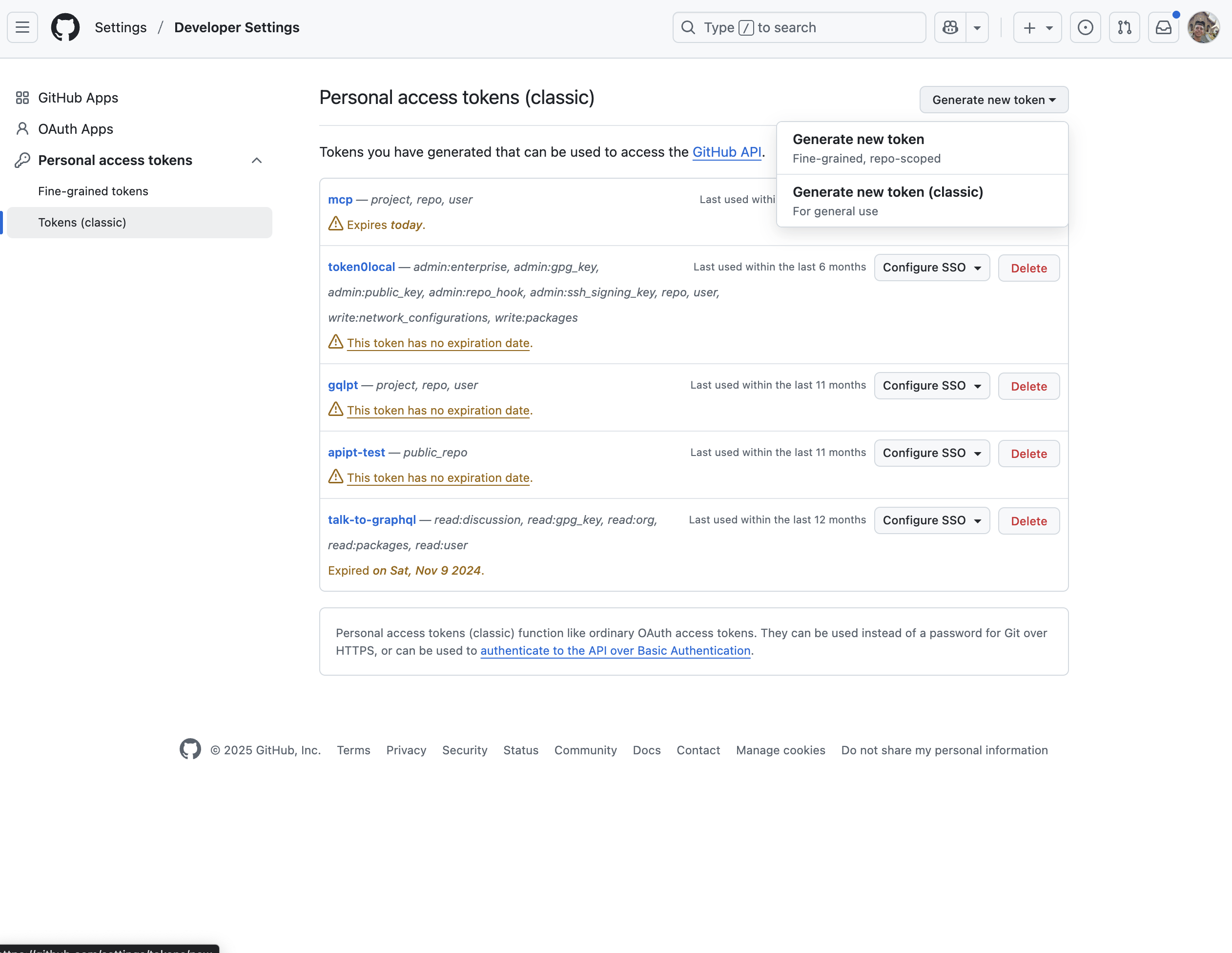
Step 1: Navigate to GitHub Token Settings
- Go to github.com/settings/tokens
- Click "Generate new token" → "Generate new token (classic)"
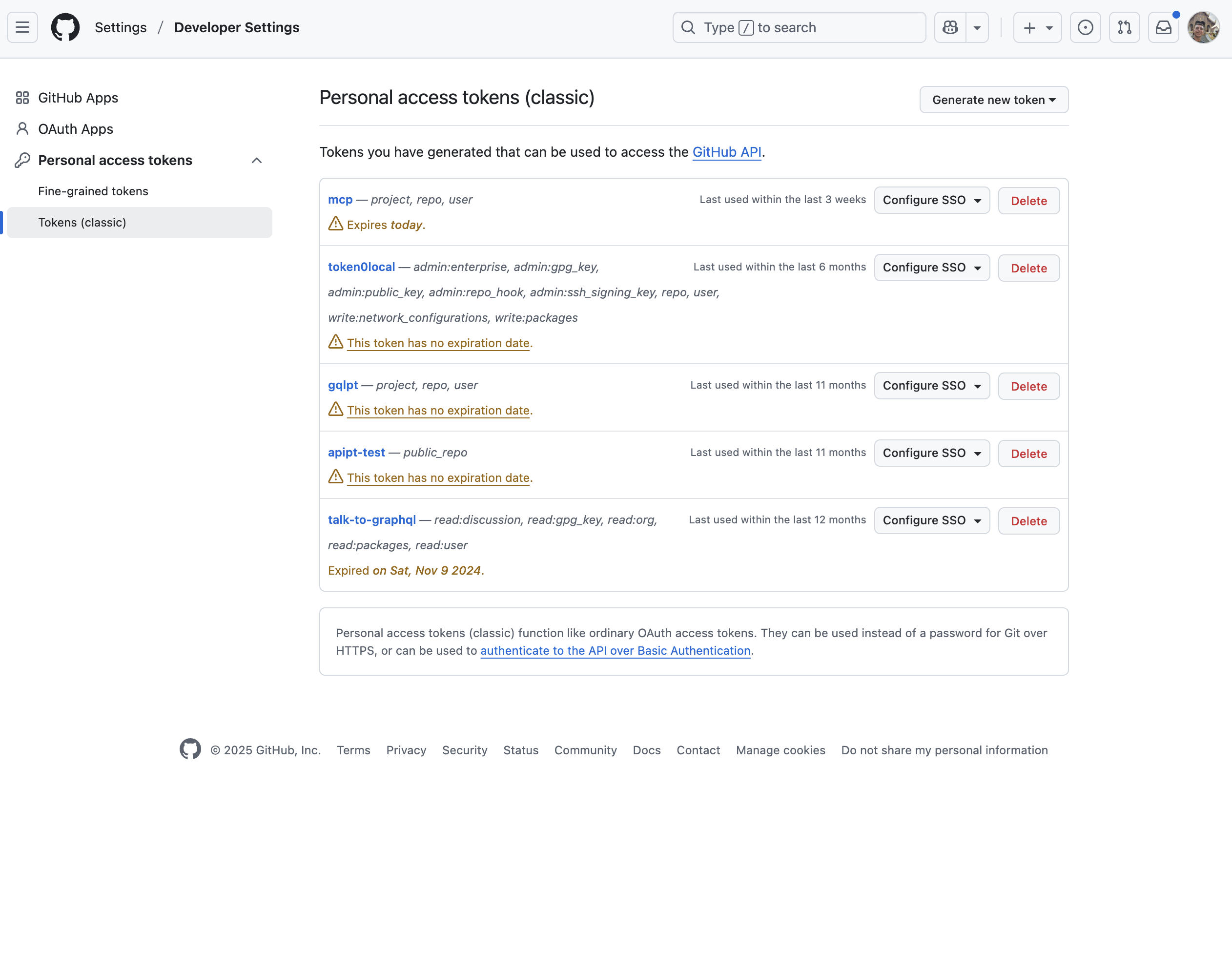
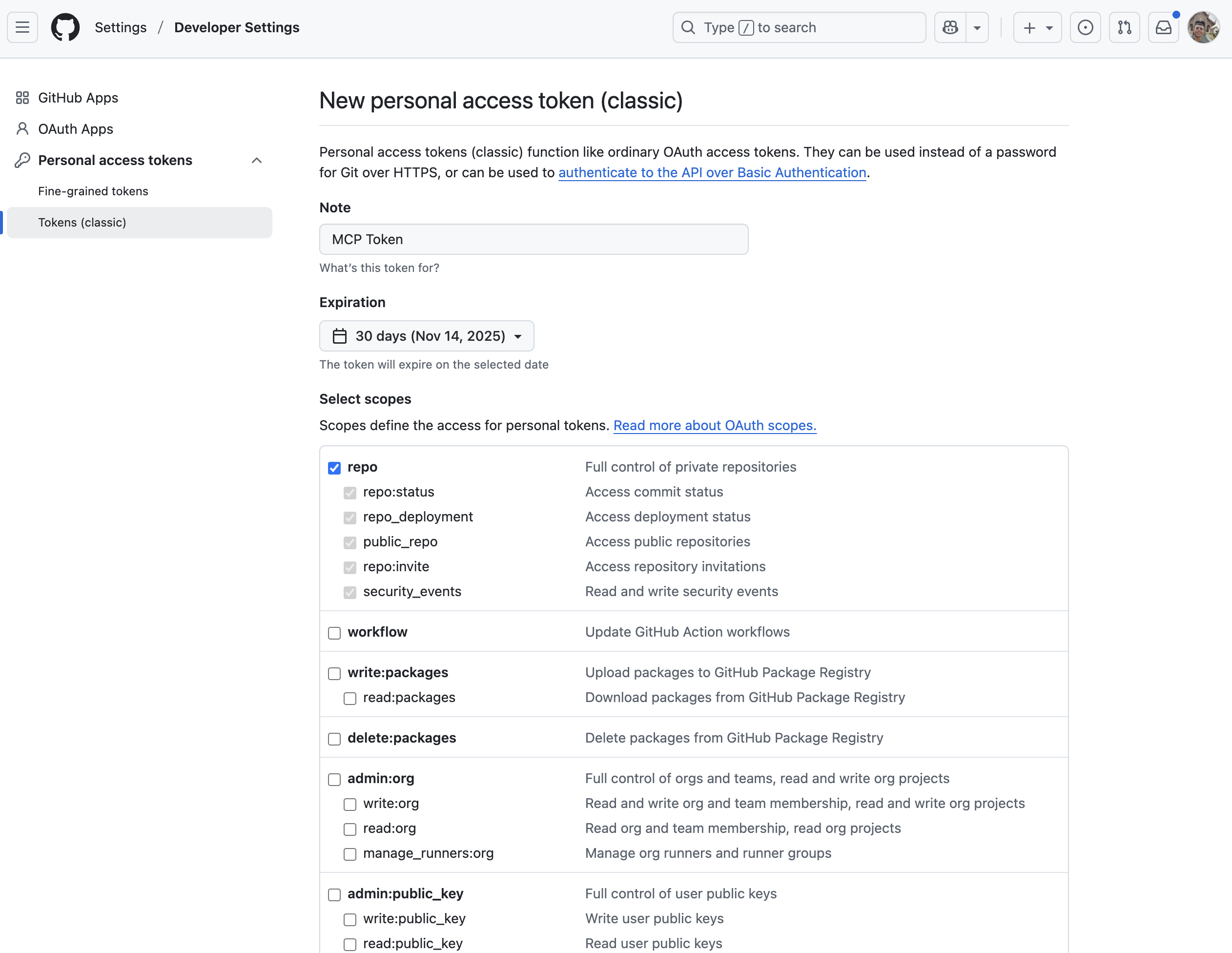
Step 2: Configure Token Permissions
Give your token a descriptive name like "MCP Token" and select scopes that suit your needs.
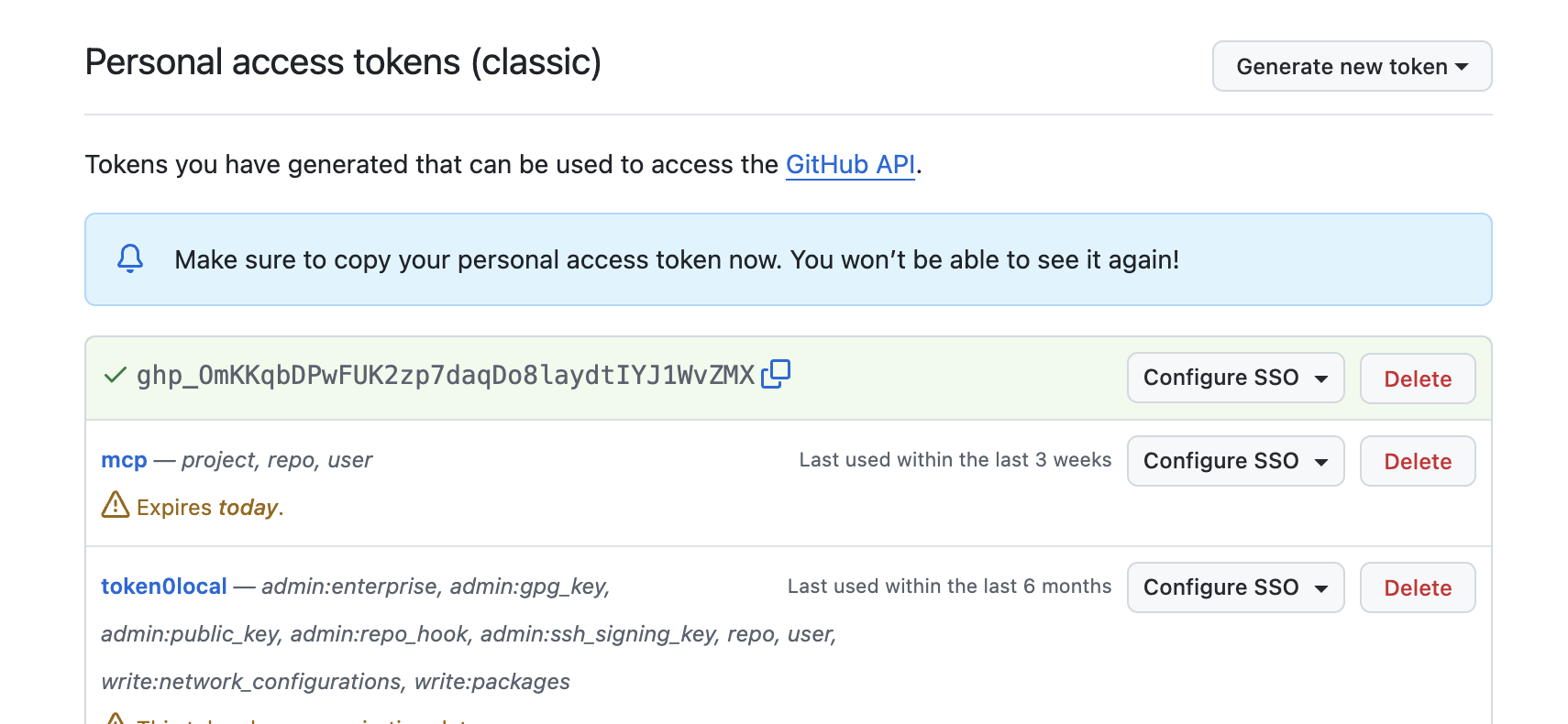
Step 3: Generate and Save Your Token
- Click "Generate token"
- IMPORTANT: Copy your token immediately - you won't be able to see it again!
- Save it securely (we'll use it in the next step)
Setting Up the GitHub MCP Server Locally
Step 1: Export Your GitHub Token
Open your terminal and export your GitHub token as an environment variable:
export GITHUB_PERSONAL_ACCESS_TOKEN=ghp_your_token_here
Important: Replace ghp_your_token_here with your actual token from the previous step.
To verify it's set correctly:
echo $GITHUB_PERSONAL_ACCESS_TOKEN
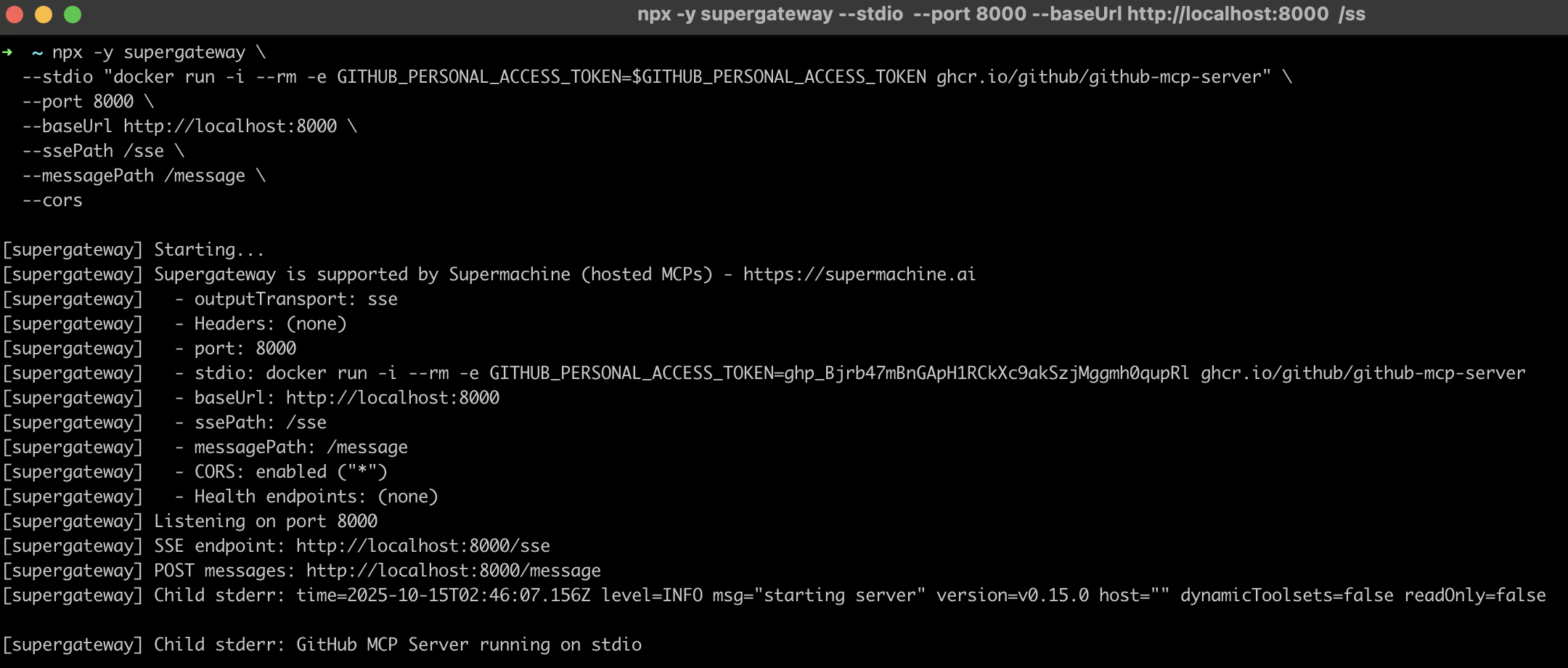
Step 2: Start the MCP Gateway with Docker
Now we'll start the GitHub MCP server using Docker through the supergateway:
npx -y supergateway \
--stdio "docker run -i --rm -e GITHUB_PERSONAL_ACCESS_TOKEN=$GITHUB_PERSONAL_ACCESS_TOKEN ghcr.io/github/github-mcp-server" \
--port 8000 \
--baseUrl http://localhost:8000 \
--ssePath /sse \
--messagePath /message \
--cors
What this command does:
npx -y supergateway- Runs the supergateway CLI tool--stdio- Specifies the Docker command to run the GitHub MCP server--port 8000- The port where the MCP server will listen--baseUrl http://localhost:8000- The base URL for the server--ssePath /sse- Server-Sent Events endpoint path for real-time updates--messagePath /message- Message handling endpoint path for sending commands--cors- Enables CORS for MCP Connect and other browser-based clients
Understanding SSE Transport:
The supergateway uses SSE (Server-Sent Events) as the output transport. This means:
- Real-time, unidirectional communication from server to client
- Automatic reconnection on connection loss
- Perfect for streaming MCP tool responses
- Lower overhead than WebSockets for this use case
Keep this terminal window open—the server needs to stay running!
You should see output like:
[supergateway] Starting...
[supergateway] - outputTransport: sse
[supergateway] - port: 8000
[supergateway] - baseUrl: http://localhost:8000
[supergateway] - ssePath: /sse
[supergateway] - messagePath: /message
[supergateway] - CORS: enabled ("*")
[supergateway] Listening on port 8000
[supergateway] SSE endpoint: http://localhost:8000/sse
[supergateway] POST messages: http://localhost:8000/message
[supergateway] Child stderr: GitHub MCP Server running on stdio
Step 3: Configure Claude Desktop
Find your Claude Desktop configuration file:
- macOS:
~/Library/Application Support/Claude/claude_desktop_config.json - Windows:
%APPDATA%/Claude/claude_desktop_config.json
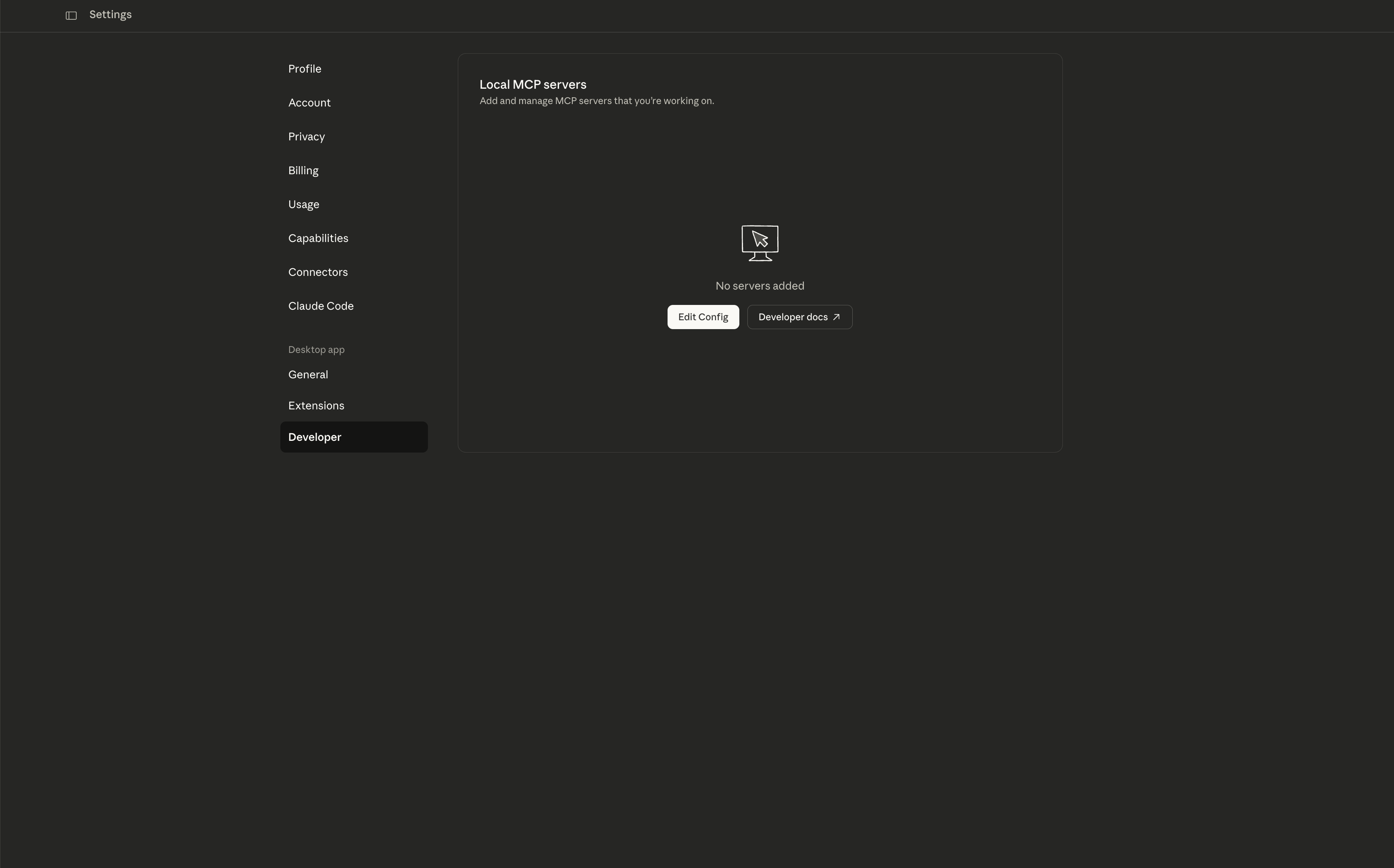
Add this configuration:
{
"mcpServers": {
"github-mcp-local": {
"command": "npx",
"args": [
"-y",
"mcp-remote@latest",
"http://localhost:8000/sse",
"--transport",
"sse",
"--allow-http"
]
}
}
}
Step 4: Restart Claude Desktop and Test
- Completely quit Claude Desktop
- Relaunch the application
- You should see a 🔧 tools indicator in Claude's input area
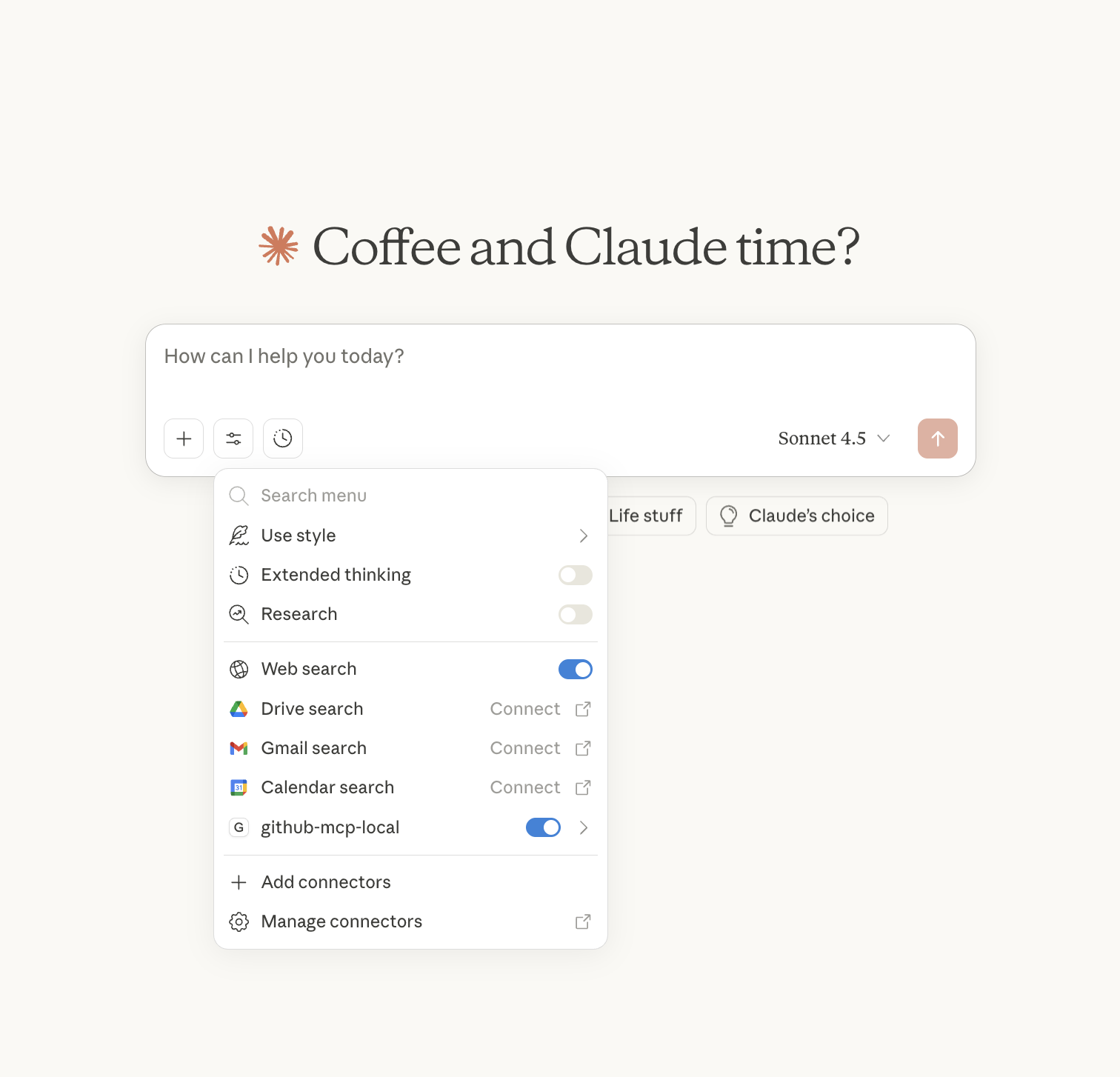
Test with these prompts:
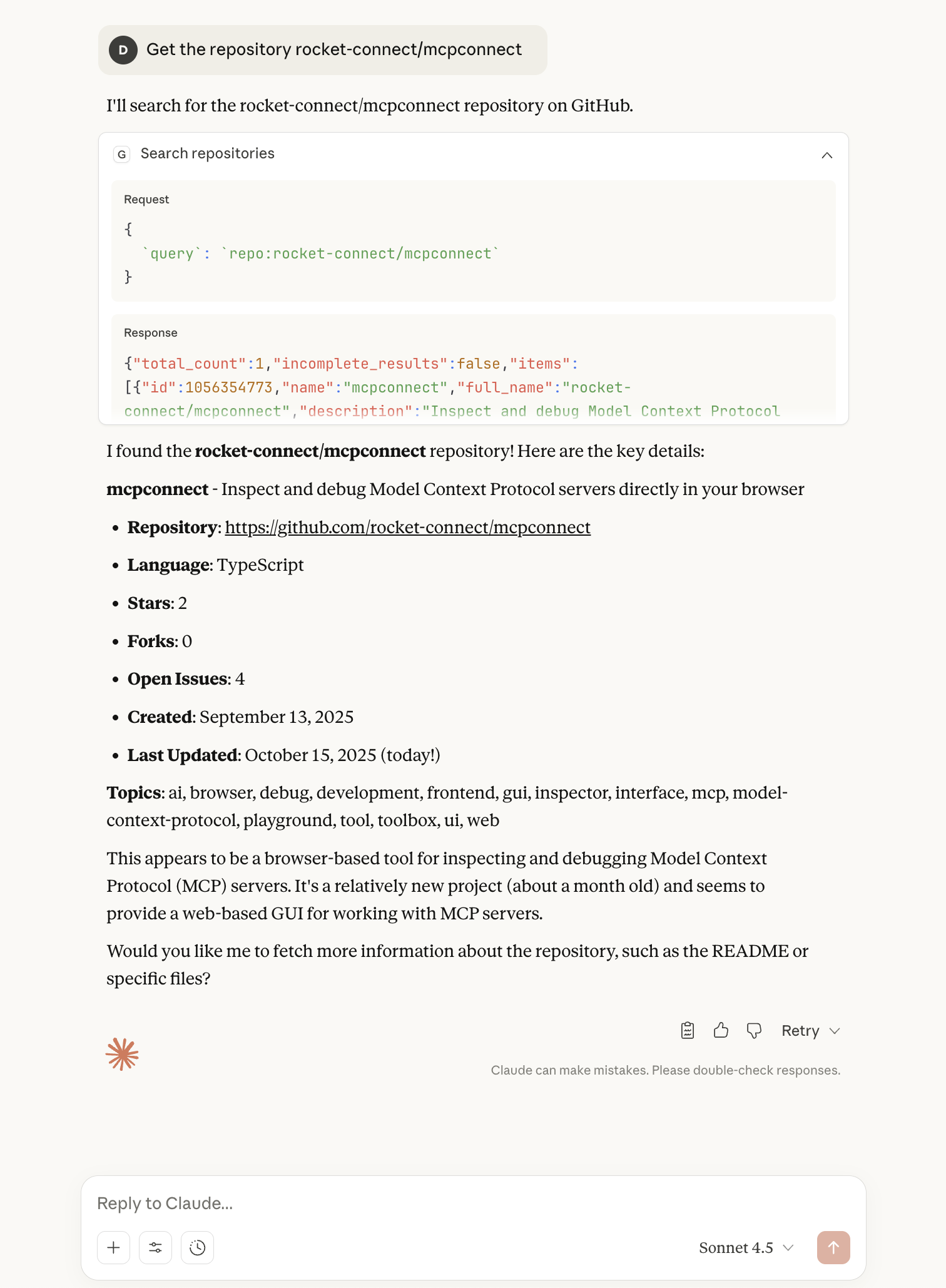
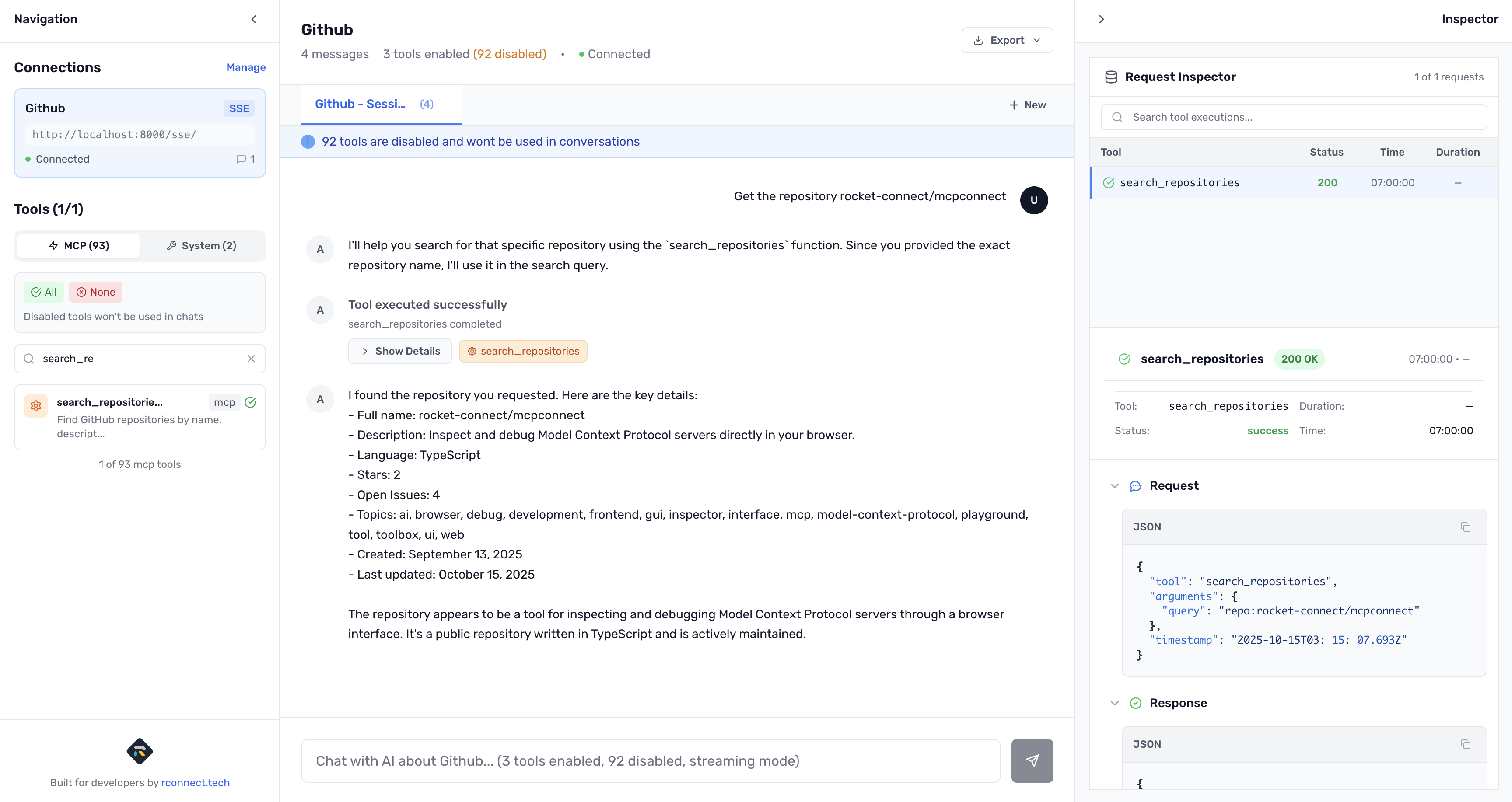
Get the repository rocket-connect/mcpconnect
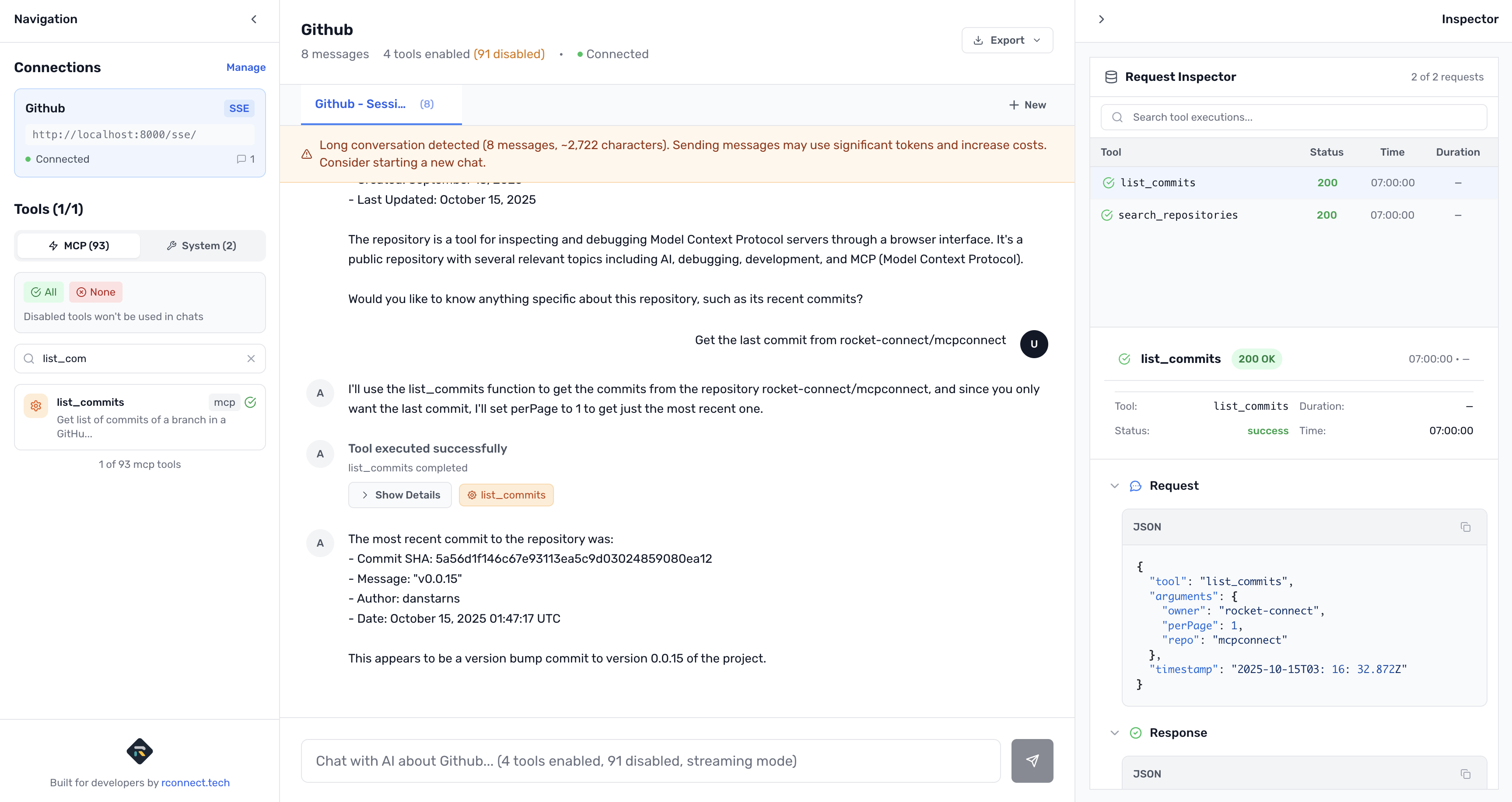
Get the last commit from rocket-connect/mcpconnect
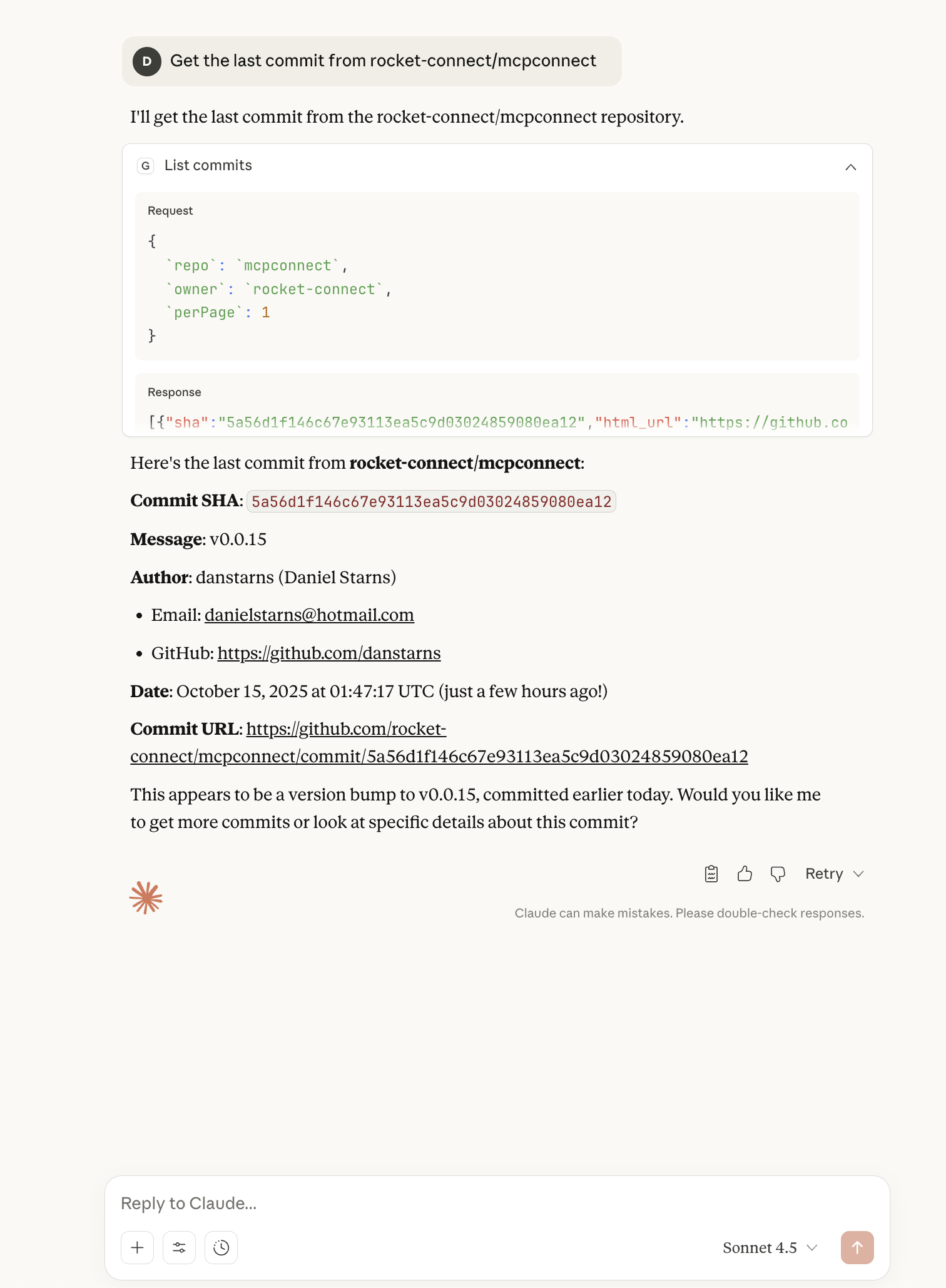
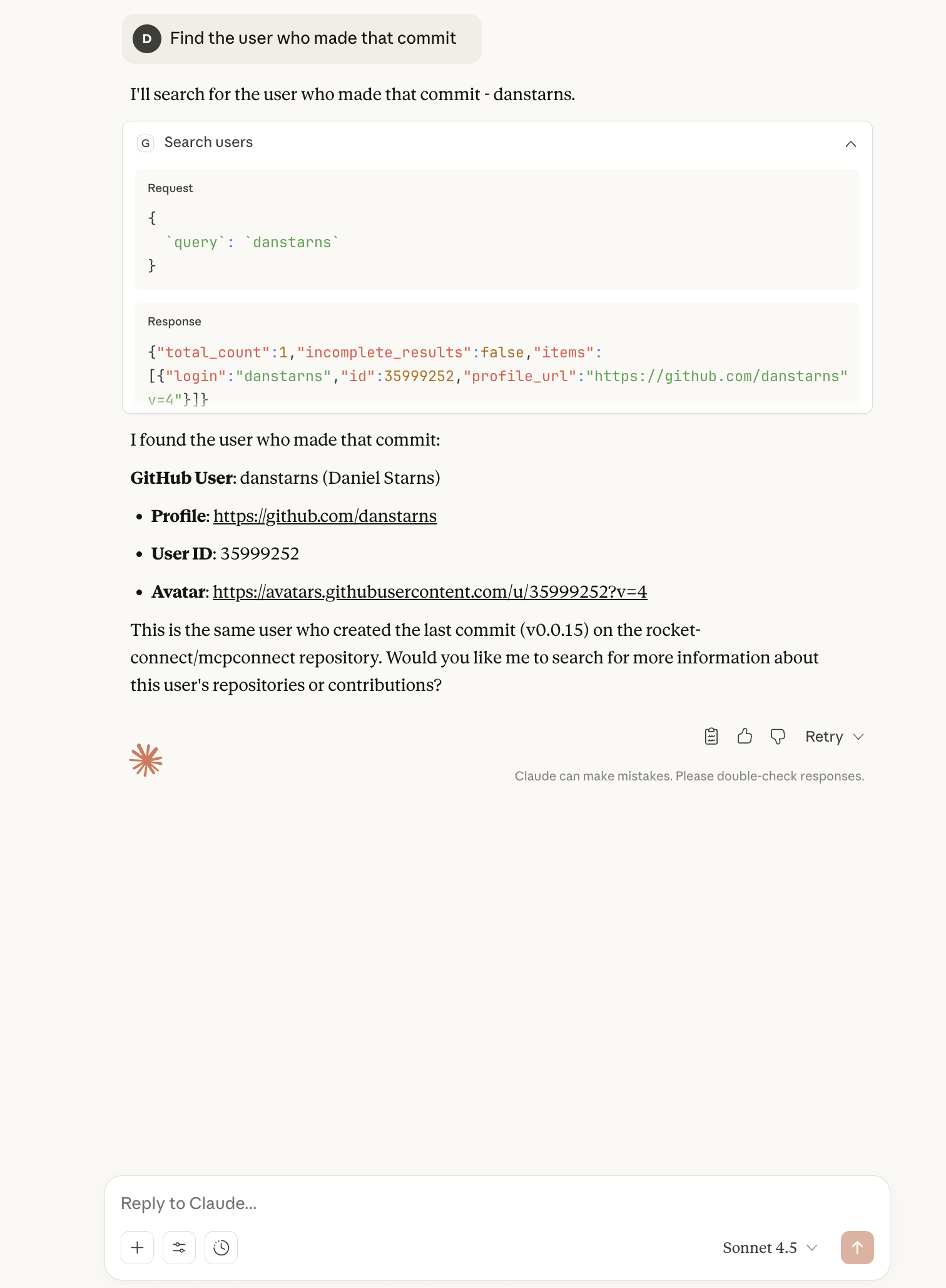
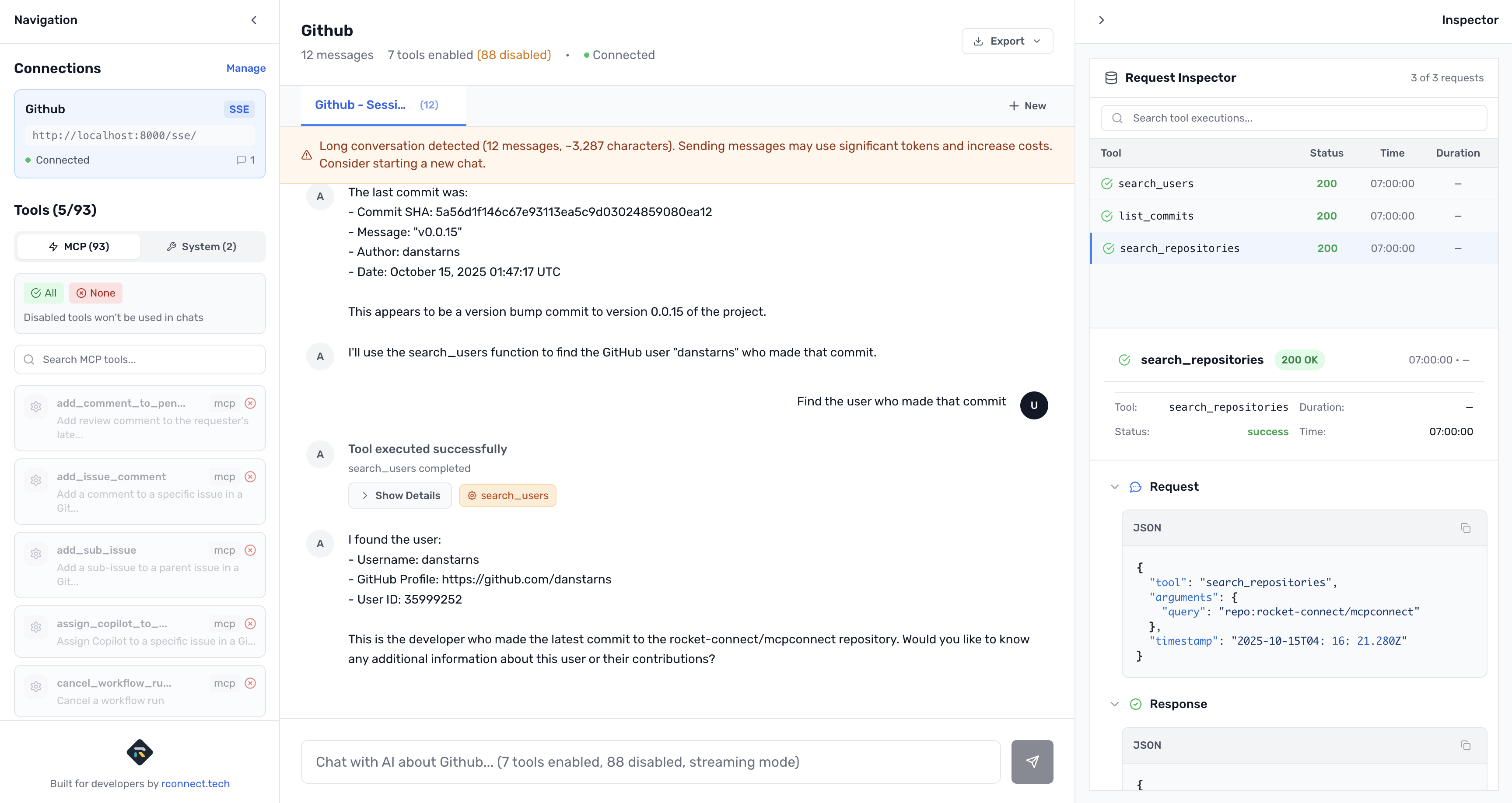
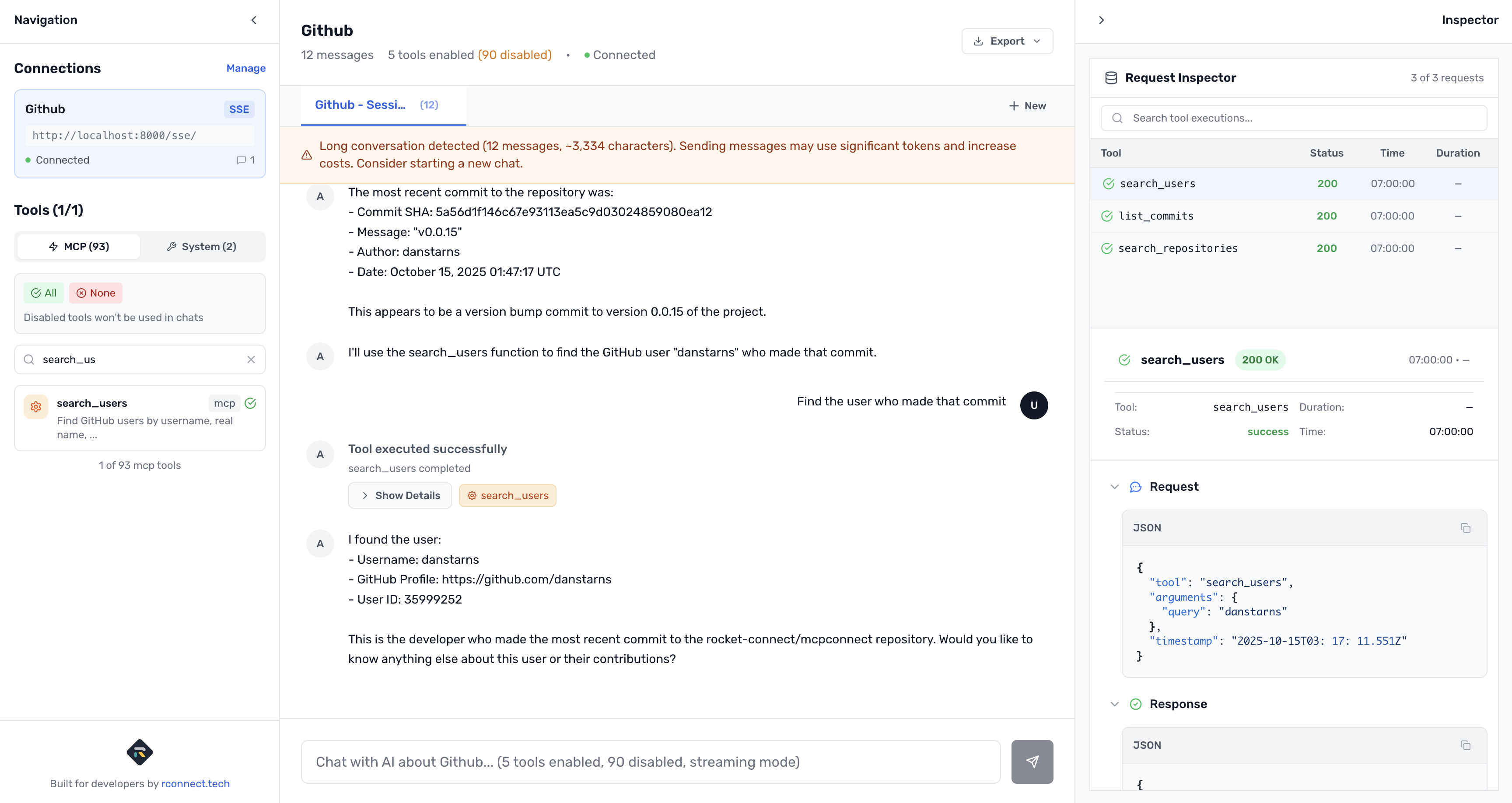
Find the user who made that commit
Why MCP Connect for Local Development?
While Claude Desktop provides a great experience for using MCP servers, MCP Connect is purpose-built for development workflows with powerful capabilities that save you time, tokens, and money.
The Token Consumption Challenge
Every tool you connect to an AI consumes tokens in each request—even if you don't use it. Here's why this matters with the GitHub MCP server:
GitHub MCP Server Tools include:
create_or_update_file- Create or update files in repositoriespush_files- Push multiple files to a repositorysearch_repositories- Search for repositoriescreate_repository- Create a new repositoryget_file_contents- Get contents of a filecreate_issue- Create a new issuecreate_pull_request- Create a new pull requestfork_repository- Fork a repositorycreate_branch- Create a new branch- And many more...
Each tool definition adds approximately 200-400 tokens to every AI request. With 90+ GitHub tools active:
- ~6,000+ tokens consumed per request just for tool definitions
- In a 10-message conversation: 60,000+ tokens on tool overhead alone
- Before you know it, you've burned through your API limits
This is where MCP Connect becomes essential.
Smart Tool Management: The MCP Connect Solution
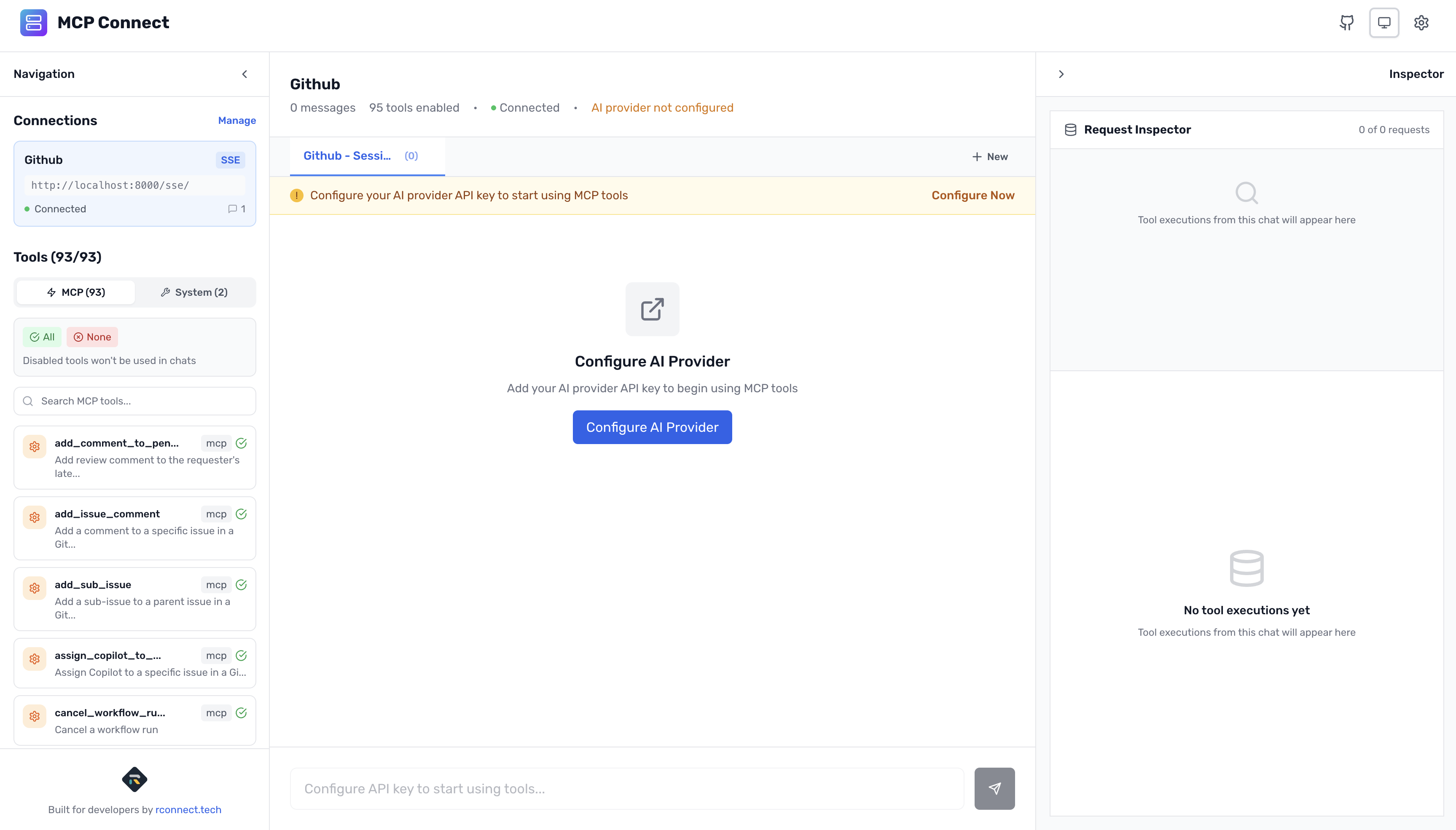
MCP Connect gives you granular control over which tools are active, dramatically reducing token consumption and costs:
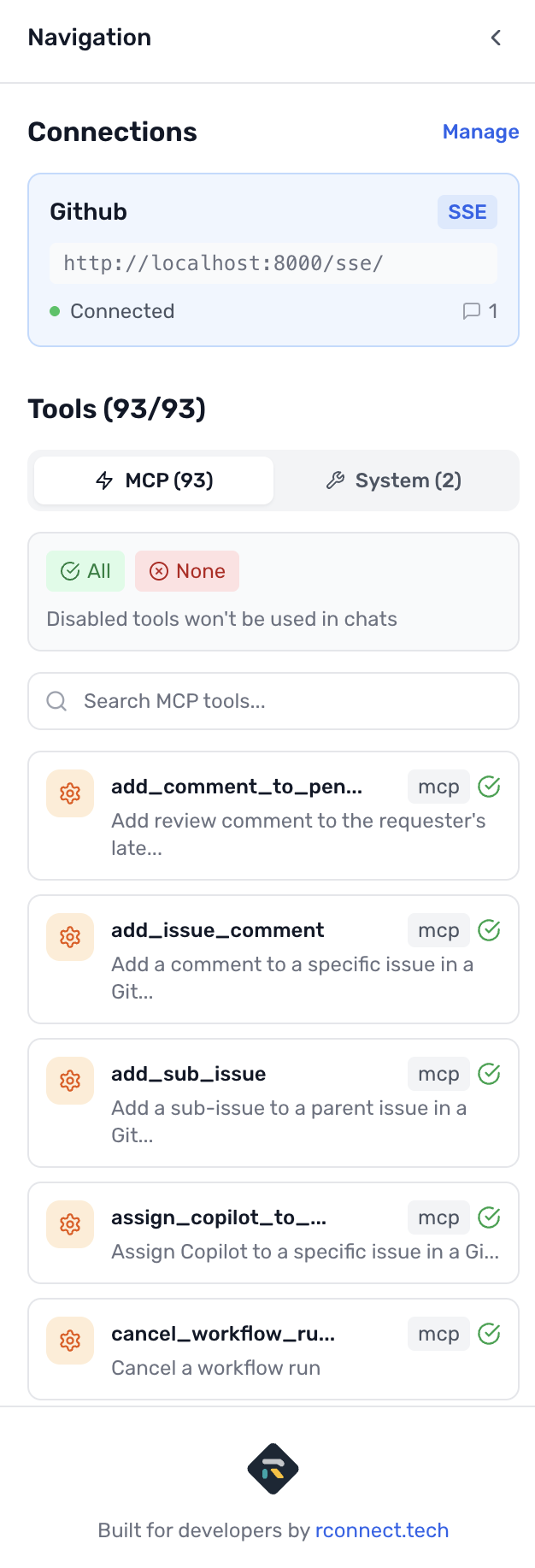
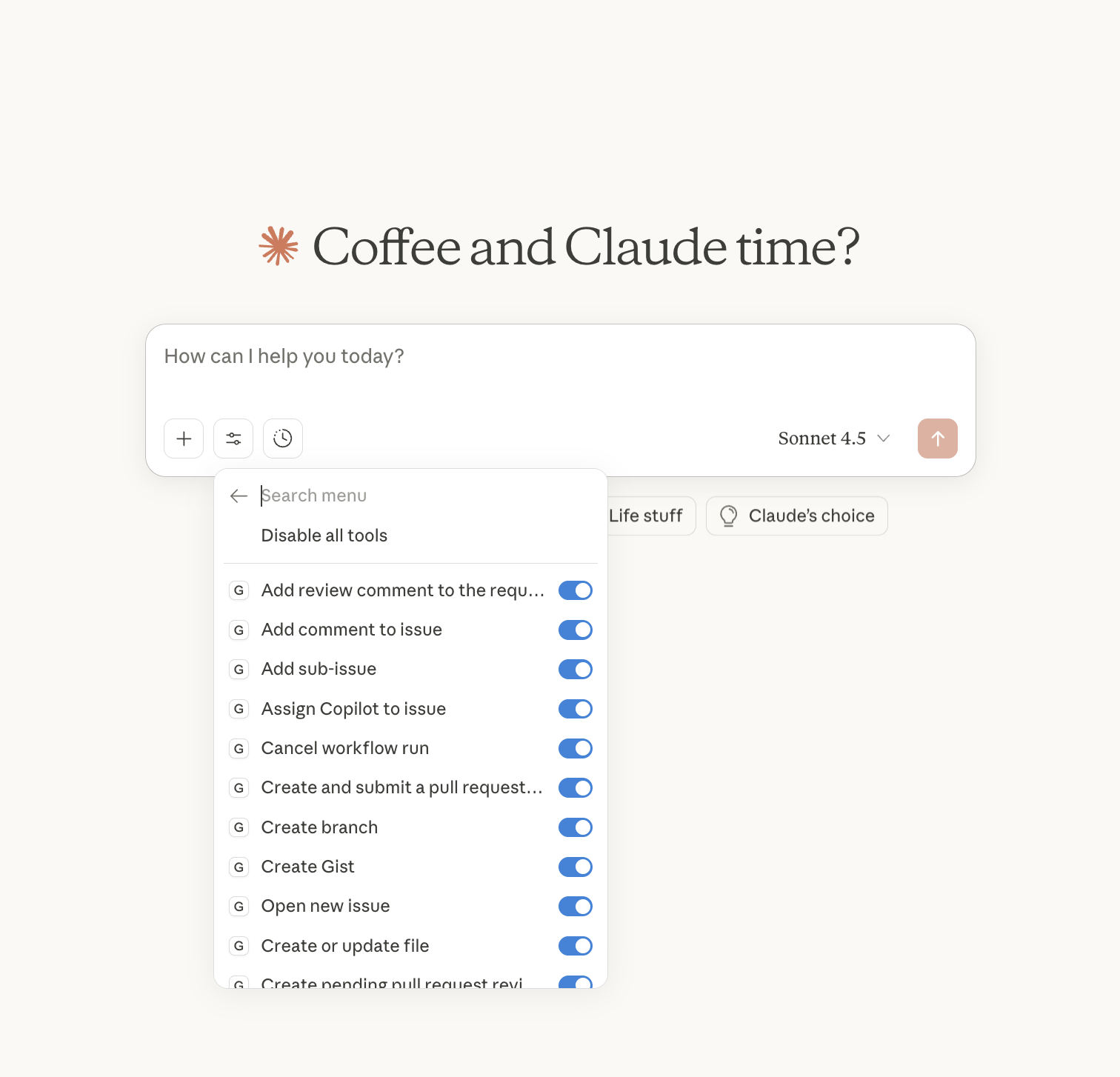
Visual Tool Control Panel
- See all available GitHub tools in an organized sidebar
- One-click enable/disable for each individual tool
- Bulk operations: Enable all, disable all, or toggle selected tools
- Real-time counters showing enabled vs. disabled tool status
- Separate tabs for MCP tools and built-in system tools
Active Tool Management Required
Important: MCP Connect doesn't automatically manage tools for you—that would defeat the purpose of giving you control. Instead:
- You decide which tools to enable based on your current task
- You toggle tools on/off through the visual interface
- You optimize for your specific workflow and token budget
- You save money by only enabling what you actually need
Step-by-Step Tool Management
When you first connect to GitHub MCP:
- All tools are enabled by default (sidebar shows: 90+/90+ tools)
- You see a clear list of available tools with descriptions
- Tool categories and usage hints help you understand each tool's purpose
To optimize your workflow:
- Identify your task: What are you trying to accomplish?
- Disable unused tools: Click to toggle off tools you don't need
- Monitor your savings: Watch the enabled/disabled count update
- Adjust as needed: Enable tools when your task changes
Example workflow:
1. Connect to GitHub → See "90/90 tools enabled"
2. Click "Disable All" → Now "0/90 tools enabled"
3. Working on issues? Enable only create_issue, list_issues → "2/90 tools enabled"
4. Need to review code? Disable issue tools, enable get_file_contents, search_code → Still "2/90 tools"
5. Ready to create a PR? Switch to create_pull_request → Still just a few tools active
Additional Development Benefits
1. Protocol Inspection Panel
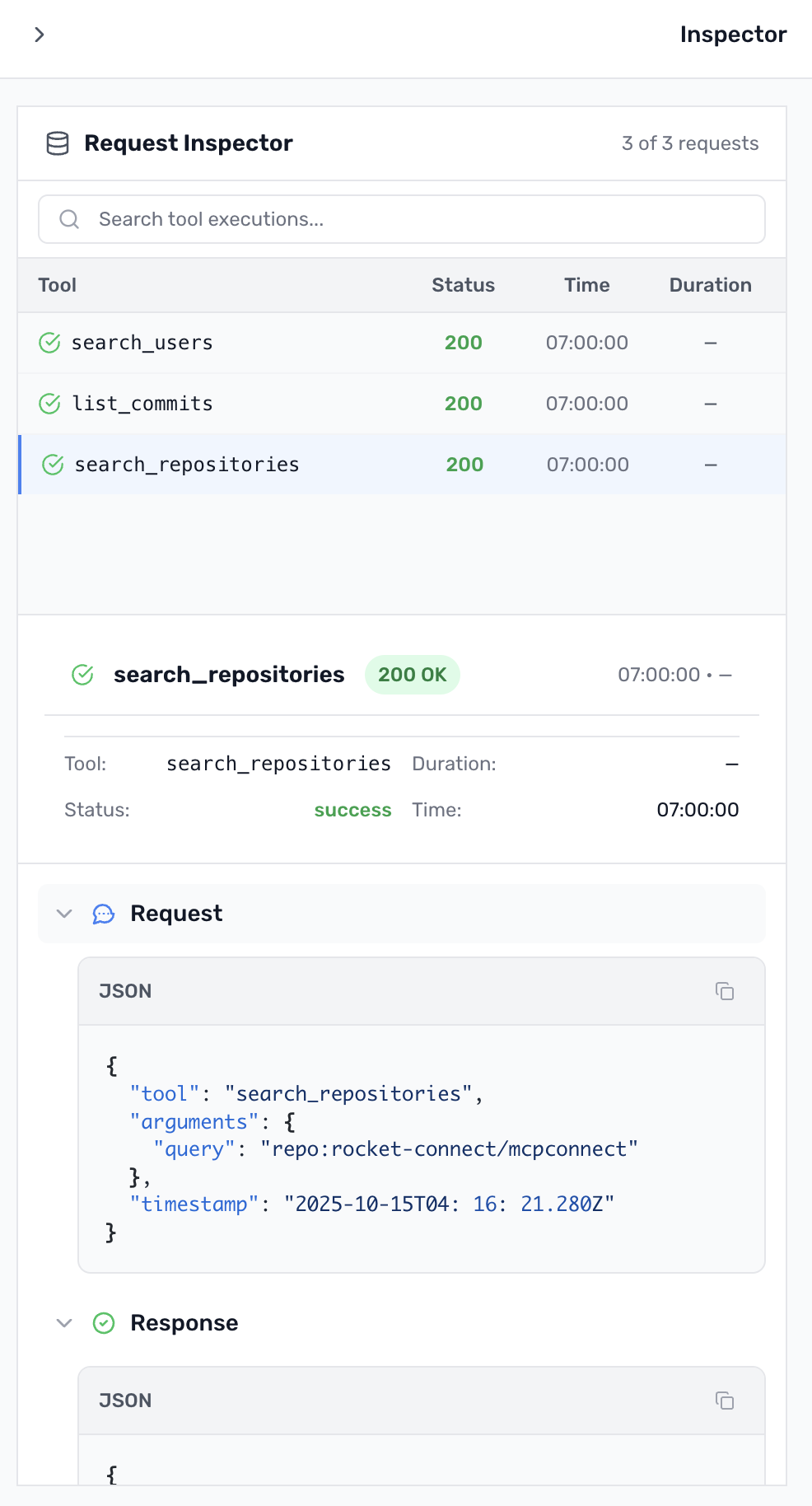
- See the raw MCP requests and responses in real-time
- Debug exactly what's being sent to GitHub's API
- Track execution timing for performance optimization
- Identify and fix issues before they reach production
2. Conversation Management
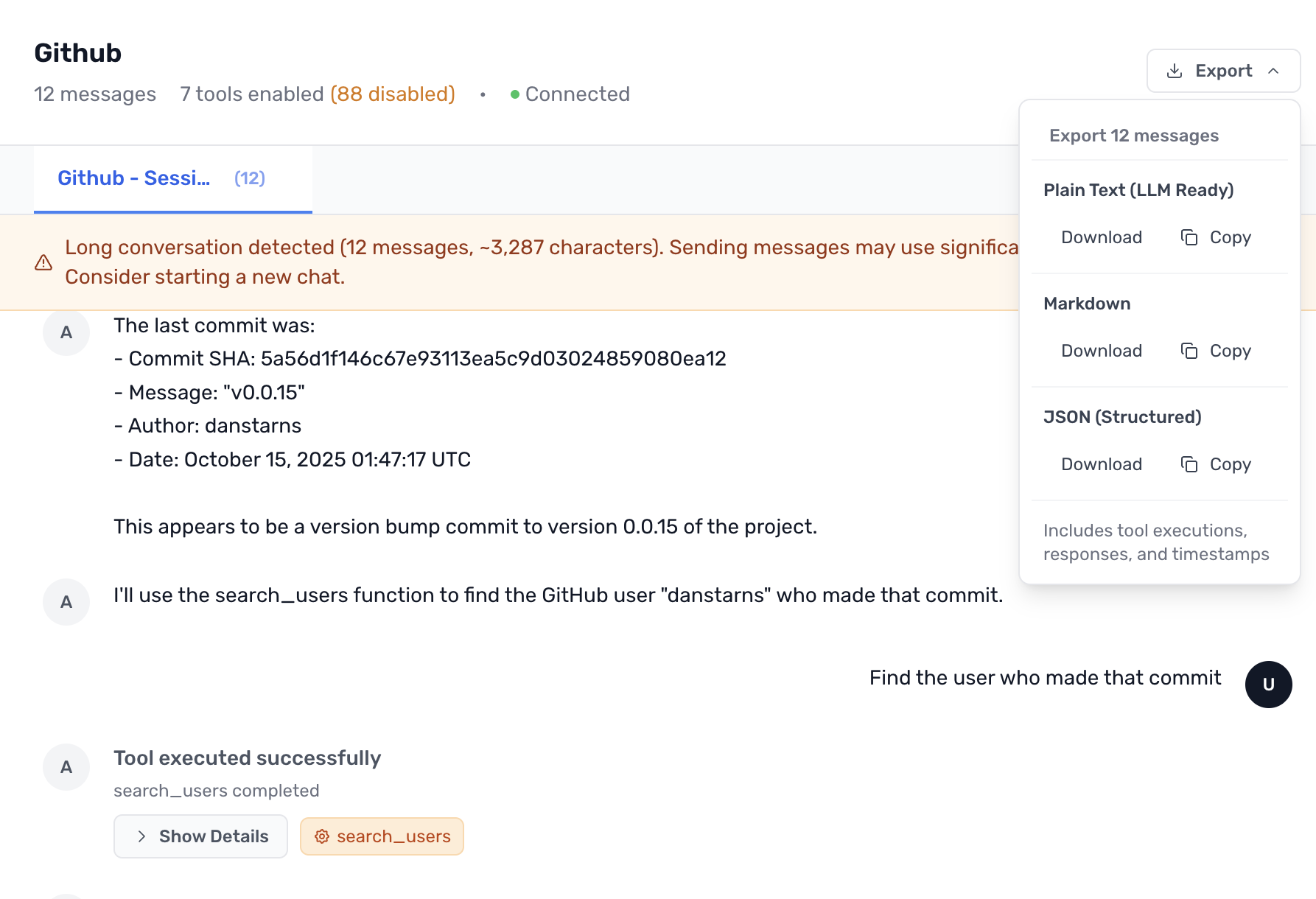
- Create multiple chat sessions with different tool configurations
- Export conversations in JSON, Markdown, or Plain Text
- Document your development process automatically
- Share debugging sessions with your team
3. Built-in System Tools
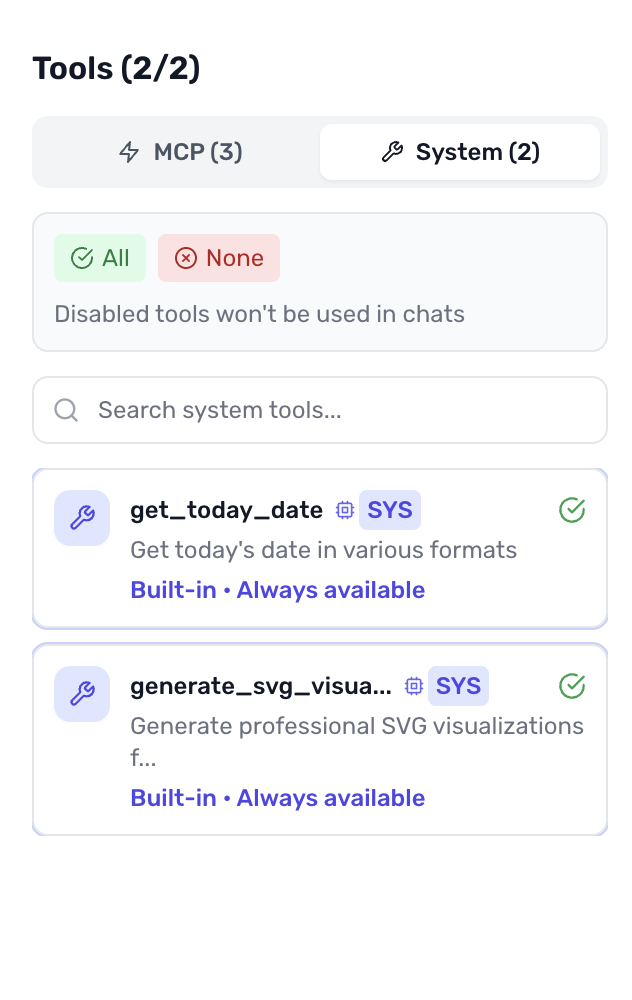
- Utility tools for data transformation and visualization
- Markdown rendering for viewing README files
- Code syntax highlighting
- Independent enable/disable from GitHub tools
4. Development Warnings
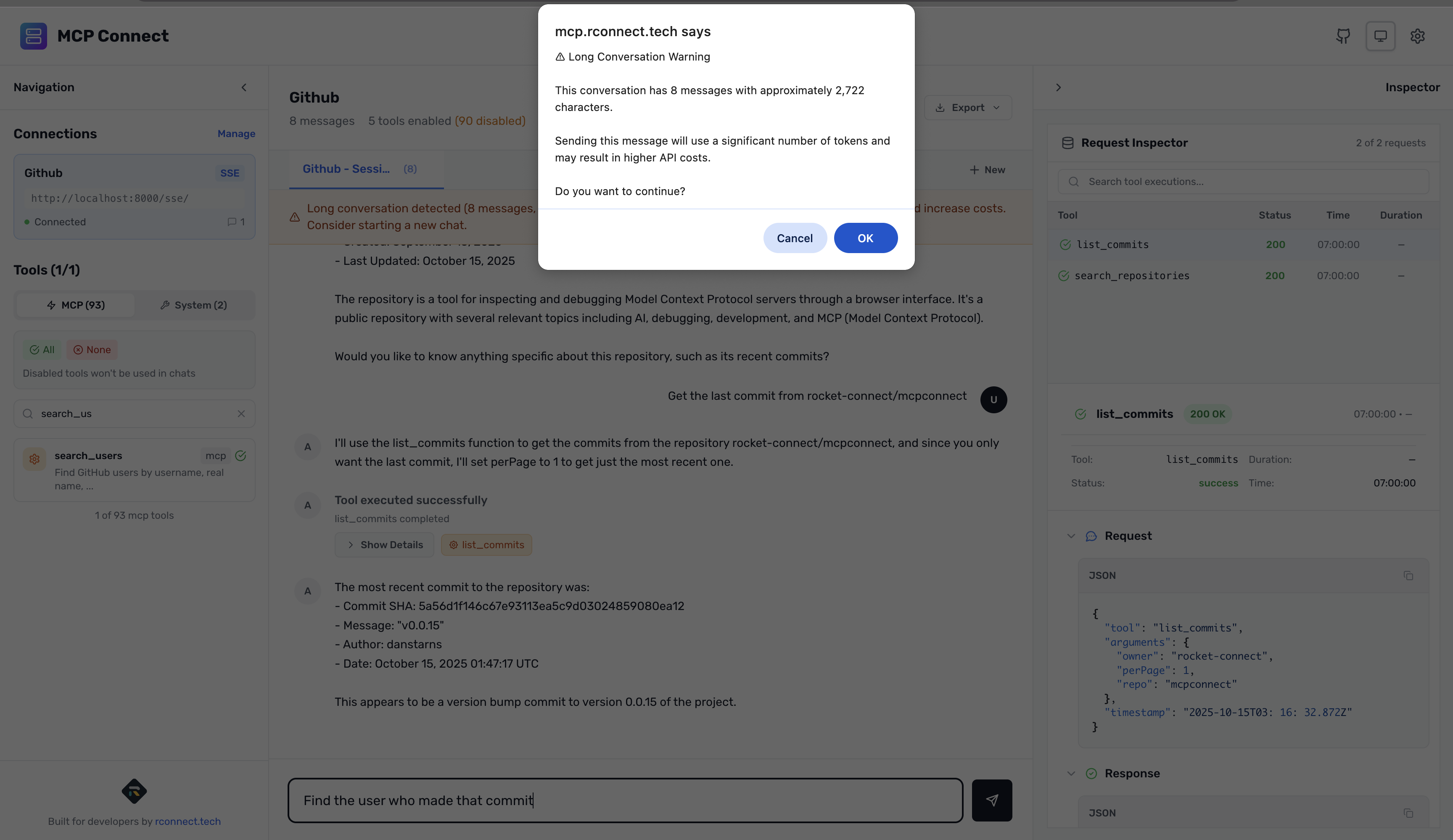
- Long conversation alerts when token usage is high
- Many tools warning when you have 5+ tools enabled
- Real-time token estimates for conversation length
- Prevent expensive mistakes before they happen
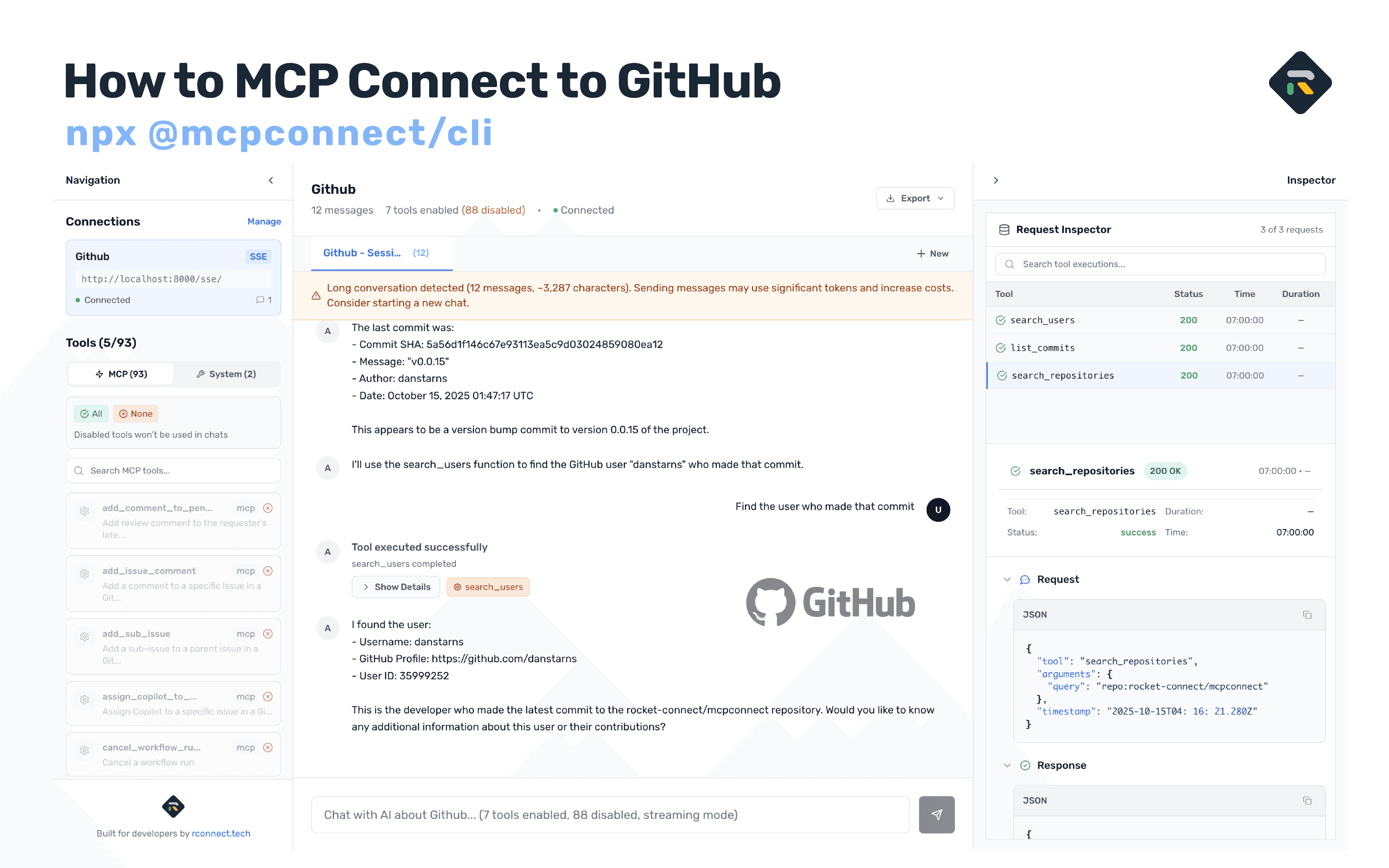
Connecting GitHub to MCP Connect
Option 1: Using MCP Connect Web (Recommended)
Visit mcp.rconnect.tech - no installation required!
Option 2: Using MCP Connect CLI
# In a new terminal window
npx @mcpconnect/cli
This starts MCP Connect on http://localhost:3001 and automatically opens your browser.
Create GitHub MCP Connection
- Click "+ New Connection" in the connections panel
- Fill in the connection details:
Connection Configuration:
Name: GitHub MCP Server
URL: http://localhost:8000/sse
Connection Type: SSE
Timeout: 60000ms
Retry Attempts: 3
- Test Connection: Click "Test Connection" to verify
- Save: Click "Create Connection"
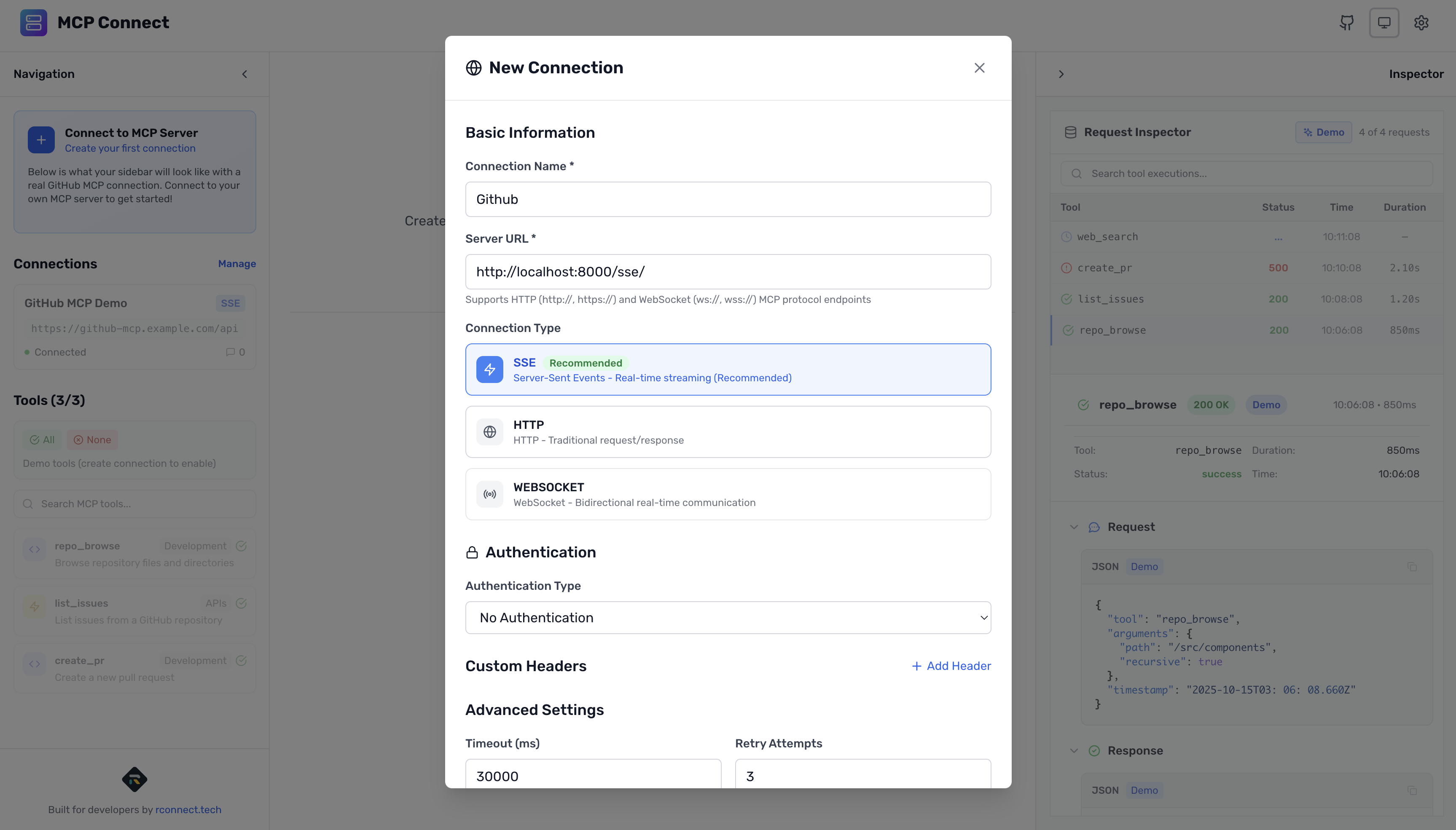
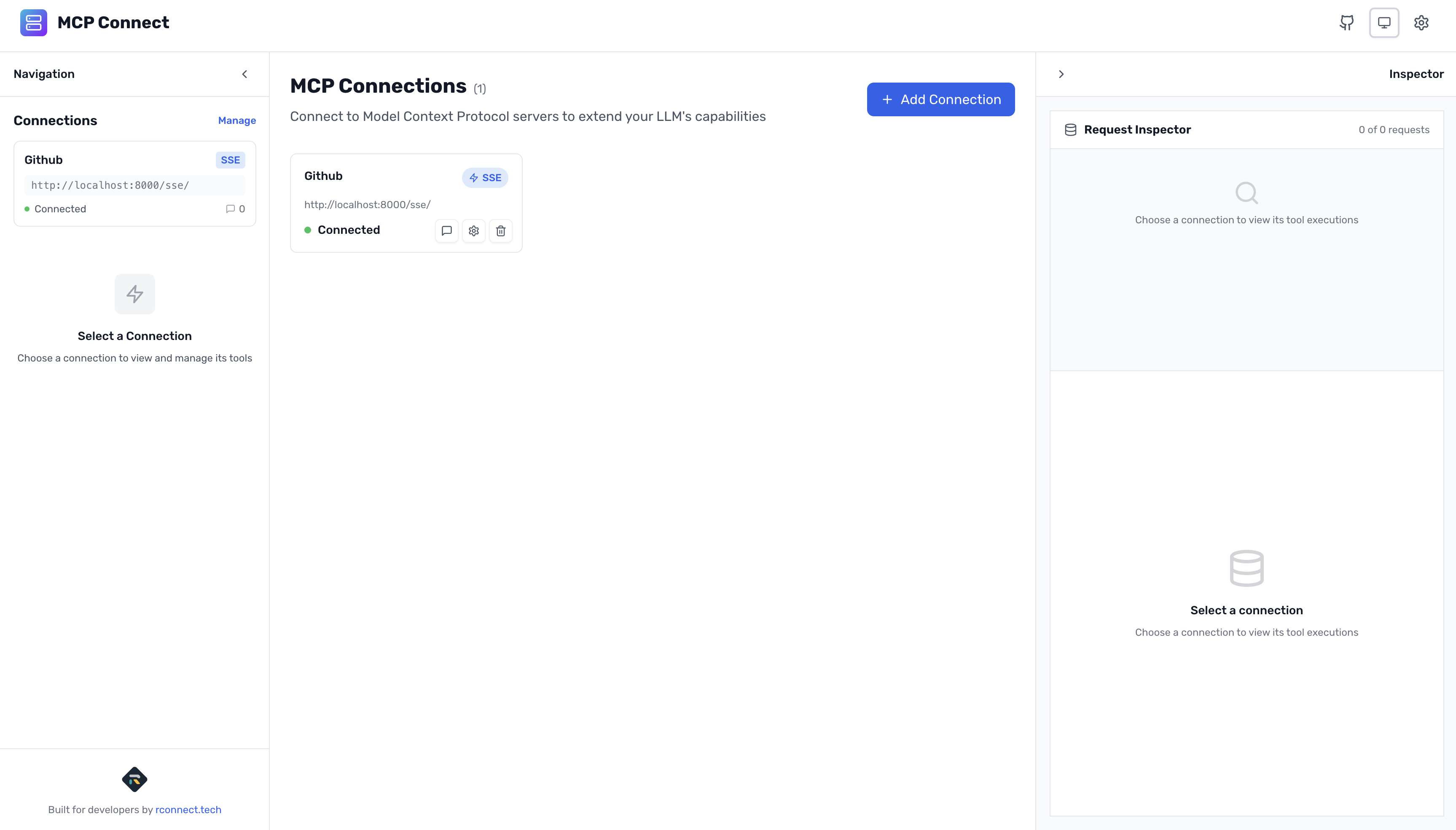
You should see:
- ✅ Connection successful
- 🔧 Tools discovered: Multiple repository, issue, and PR management tools
- 📊 Server: GitHub MCP Server
- 🌐 Transport: SSE (Server-Sent Events)
- 📍 SSE Endpoint: http://localhost:8000/sse
- 📮 Message Endpoint: http://localhost:8000/message
Configure Your AI Provider
- Click the Settings icon (⚙️) in the header
- Select Anthropic as your provider
- Enter your API key (get one at console.anthropic.com)
- Choose Claude 3.5 Sonnet (recommended for repository interactions)
- Click Test to verify your API key
- Save your configuration
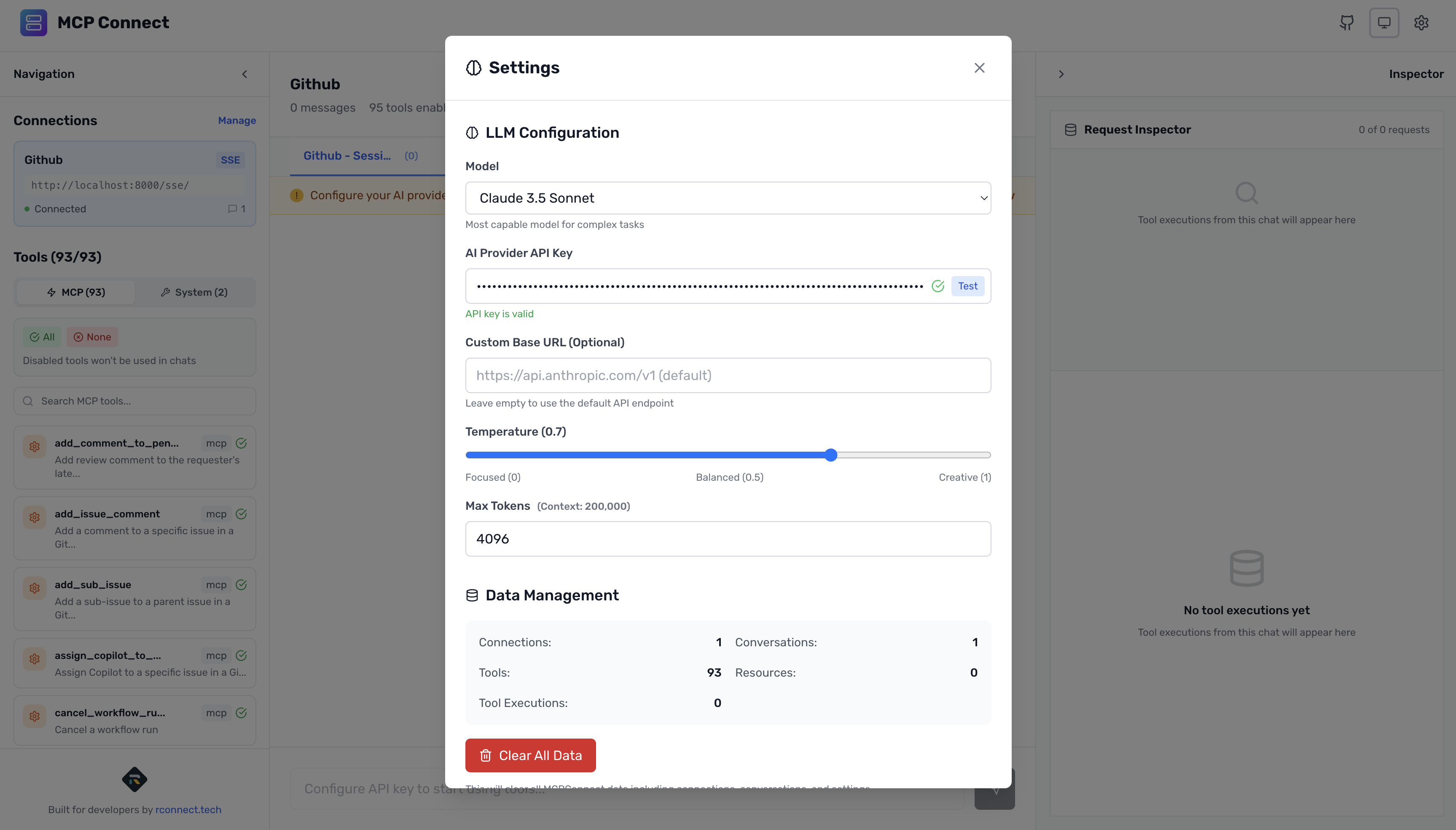
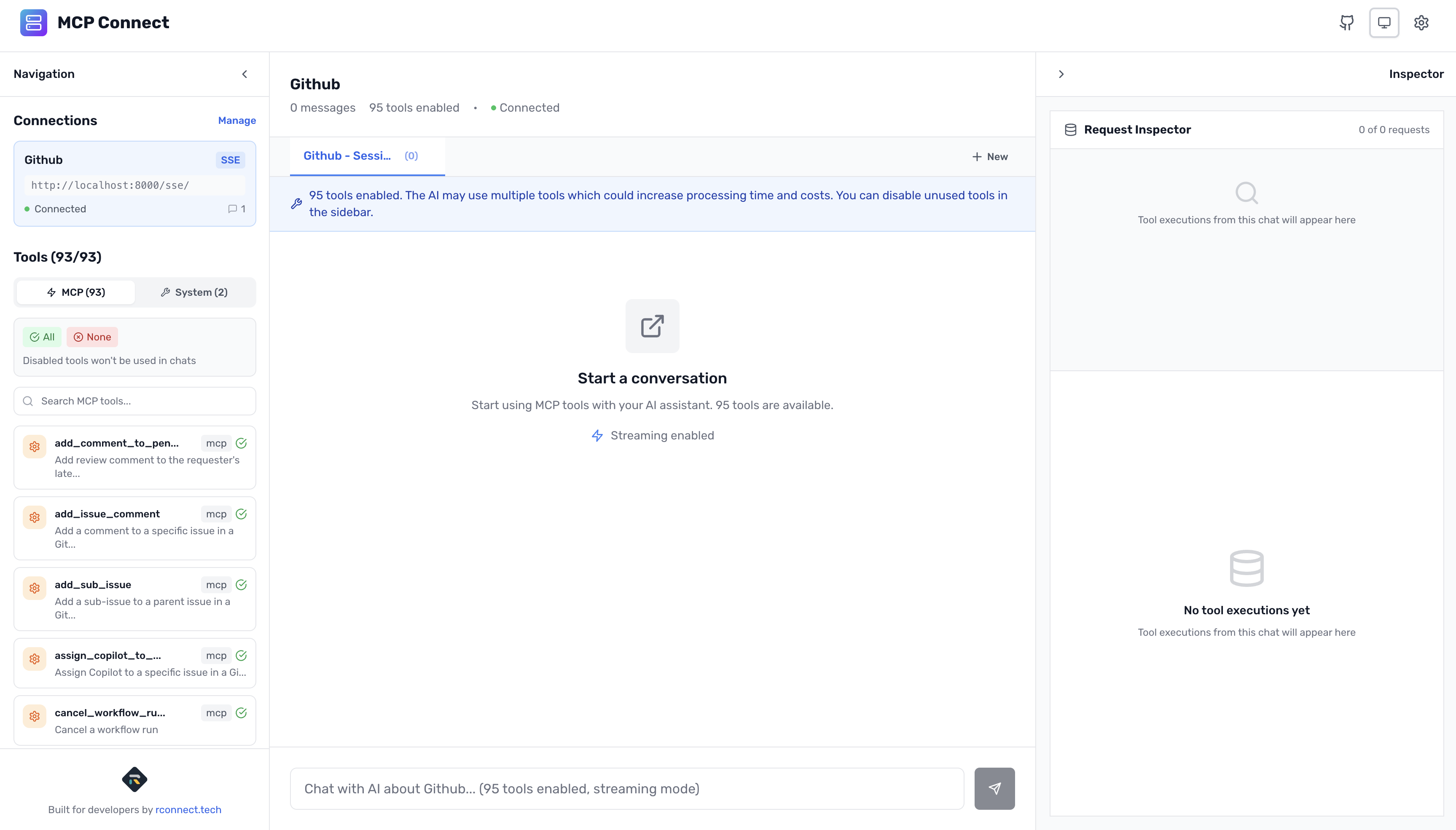
Understanding Your GitHub Tools
Once connected, the left sidebar shows your GitHub tools with full descriptions:
MCP Tools (GitHub) - 90+ tools (all enabled by default)
Key tools include:
-
Repository Management
search_repositories- Search for repositoriescreate_repository- Create new repositoriesget_repository- Get repository detailsfork_repository- Fork repositories
-
File Operations
get_file_contents- Read file contentscreate_or_update_file- Create or update filespush_files- Push multiple files at oncesearch_code- Search code across repositories
-
Issue Management
create_issue- Create new issuesupdate_issue- Update existing issueslist_issues- List repository issuesadd_issue_comment- Add comments to issues
-
Pull Request Operations
create_pull_request- Create new pull requestslist_pull_requests- List repository PRsget_pull_request- Get PR detailscreate_pull_request_review- Review pull requests
-
Branch Management
create_branch- Create new brancheslist_branches- List repository brancheslist_commits- List commit history
Testing Your GitHub Integration
Try these prompts in MCP Connect:
Get the repository rocket-connect/mcpconnect
Get the last commit from rocket-connect/mcpconnect
Find the user who made that commit
Essential Resources
Tools & Platforms
- MCP Connect Web - Browser-based GitHub MCP development
- MCP Connect CLI - Local development server
- GitHub MCP Server - Official integration
- GitHub Personal Access Tokens - Token management
- Supergateway - MCP server gateway
Documentation
- GitHub REST API - Complete API reference
- MCP Specification - Protocol details
- Claude Desktop MCP Guide - Integration docs
- Docker Documentation - Container platform guide
- Server-Sent Events (SSE) Specification - SSE protocol details
Connect with Us
We're passionate about connecting people through open source and building tools that make developers' lives easier. MCP Connect is part of our mission to enhance the open-source ecosystem and foster community engagement.
Get Involved:
- Try MCP Connect and share your feedback
- Join our YouTube community for tutorials
- Follow us on Twitter/X for updates
- Connect on LinkedIn
- Explore our open source projects
Ready to collaborate? Contact us today and let's build something great together!