GraphQL to MCP Interoperability with MCP Connect
Learn how to bridge GraphQL APIs with Model Context Protocol using MCP Connect. Convert your existing GraphQL endpoints to MCP-compatible interfaces with dynamic field selection, automatic schema introspection, and AI-powered query generation.
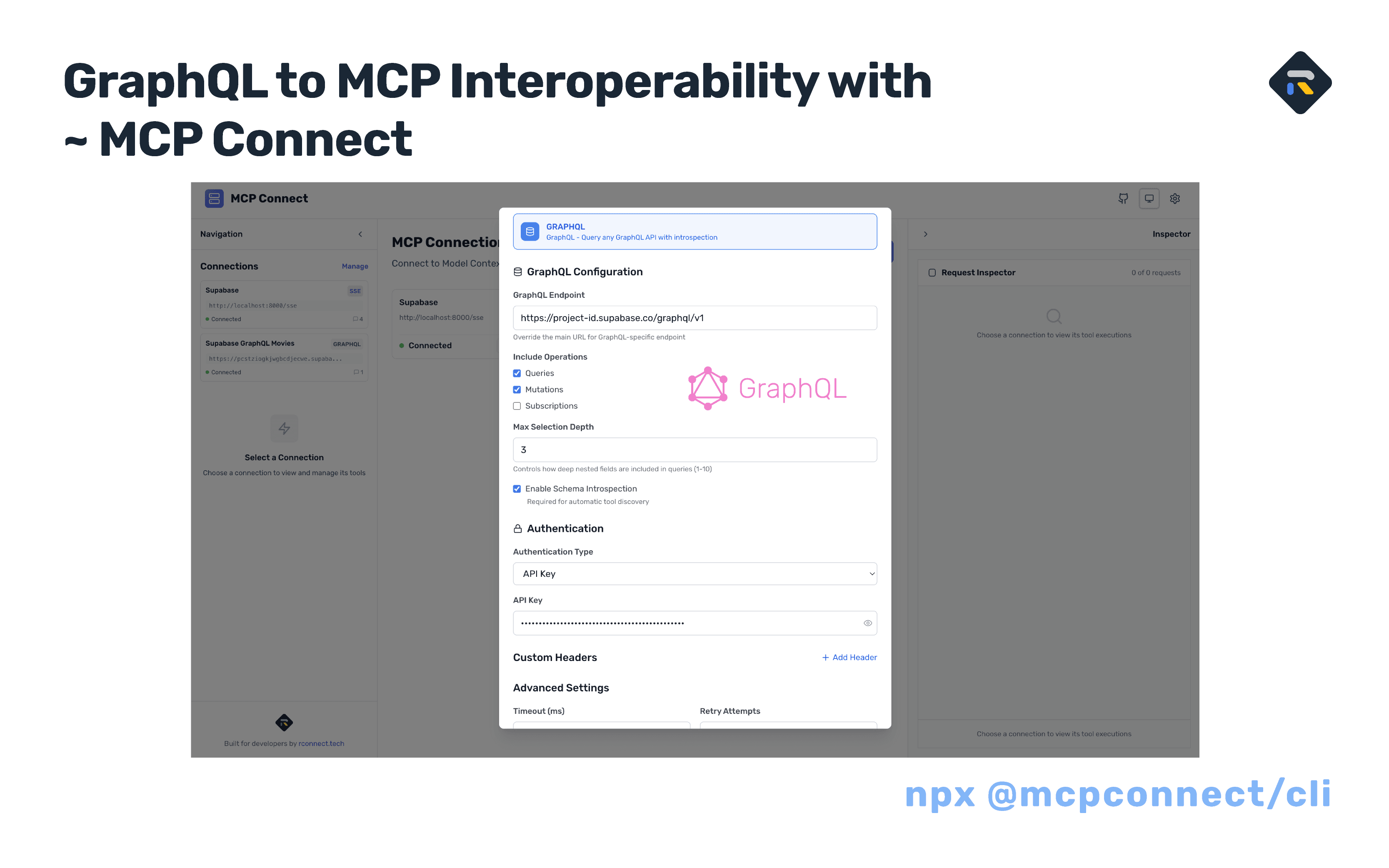
Learn how to transform your Supabase GraphQL API into an MCP-compatible interface using MCP Connect - entirely in your browser
Keen to learn more about MCP from in-person experts? Check out our upcoming MCP Bangkok (16th October 2025) and MCP Singapore (23rd October 2025) meetups.
Why We Built This: Lessons from GQLPT
After building and battle-testing GQLPT - our AI-powered GraphQL query generation tool - we discovered something important: having AI generate GraphQL queries directly is complex, error-prone, and insecure.
With GQLPT.dev, we saw firsthand the challenges:
- AI hallucinating non-existent fields
- Incorrectly nested queries causing errors
- Security vulnerabilities from unvalidated query strings
- Token waste from injecting entire schemas into prompts
The MCP Connect approach is fundamentally different and superior:
- AI calls structured tools instead of writing query strings
- Field selection happens through typed parameters, not string manipulation
- Validation occurs at the tool level, not after query generation
- Zero risk of injection attacks or malformed queries
This guide shows you the simpler, more effective, and more secure way to connect GraphQL APIs with AI.
The GraphQL and MCP Connection
If you're already using GraphQL, you're closer to Model Context Protocol (MCP) integration than you might think. Both protocols share a fundamental philosophy: giving clients precise control over what data they receive.
GraphQL pioneered this approach for traditional APIs, while MCP extends these principles to AI interactions—enabling language models to query your data sources with the same precision and flexibility.
What Makes GraphQL MCP-Ready?
GraphQL's design naturally aligns with MCP's requirements:
- Self-describing schema: Introspection reveals all available operations
- Flexible queries: Clients specify exactly what fields they need
- Type safety: Strong typing ensures predictable responses
- Single endpoint: One URL for all operations, just like MCP
This natural alignment means if you already have a GraphQL API, you're 80% of the way to MCP integration. MCP Connect bridges the remaining gap entirely in the browser—no backend changes required.
Understanding Model Context Protocol (MCP)
Model Context Protocol (MCP) is an open standard created by Anthropic that enables seamless integration between AI applications and external data sources. Think of it as a universal adapter that allows AI models like Claude to securely access and interact with your APIs, databases, and tools.
Why MCP Matters for GraphQL:
- Tool-based Interface: Convert GraphQL operations into callable tools
- Dynamic Querying: AI determines which fields to fetch based on user questions
- Schema Preservation: Your GraphQL types become MCP tool parameters
- Authentication: Standard token-based auth works seamlessly
Prerequisites
Before getting started, you'll need:
- A Supabase account (we'll create this together)
- Node.js installed for MCP Connect CLI (optional)
- A modern web browser for MCP Connect Web
Part 1: Setting Up Your Supabase Project
First, let's create a Supabase project with sample data. If you've already completed our Supabase MCP guide, you can skip to Part 2.
Step 1: Create Your Supabase Account
- Go to supabase.com
- Click "Start your project" or "Sign up"
- Sign up using GitHub, Google, or email
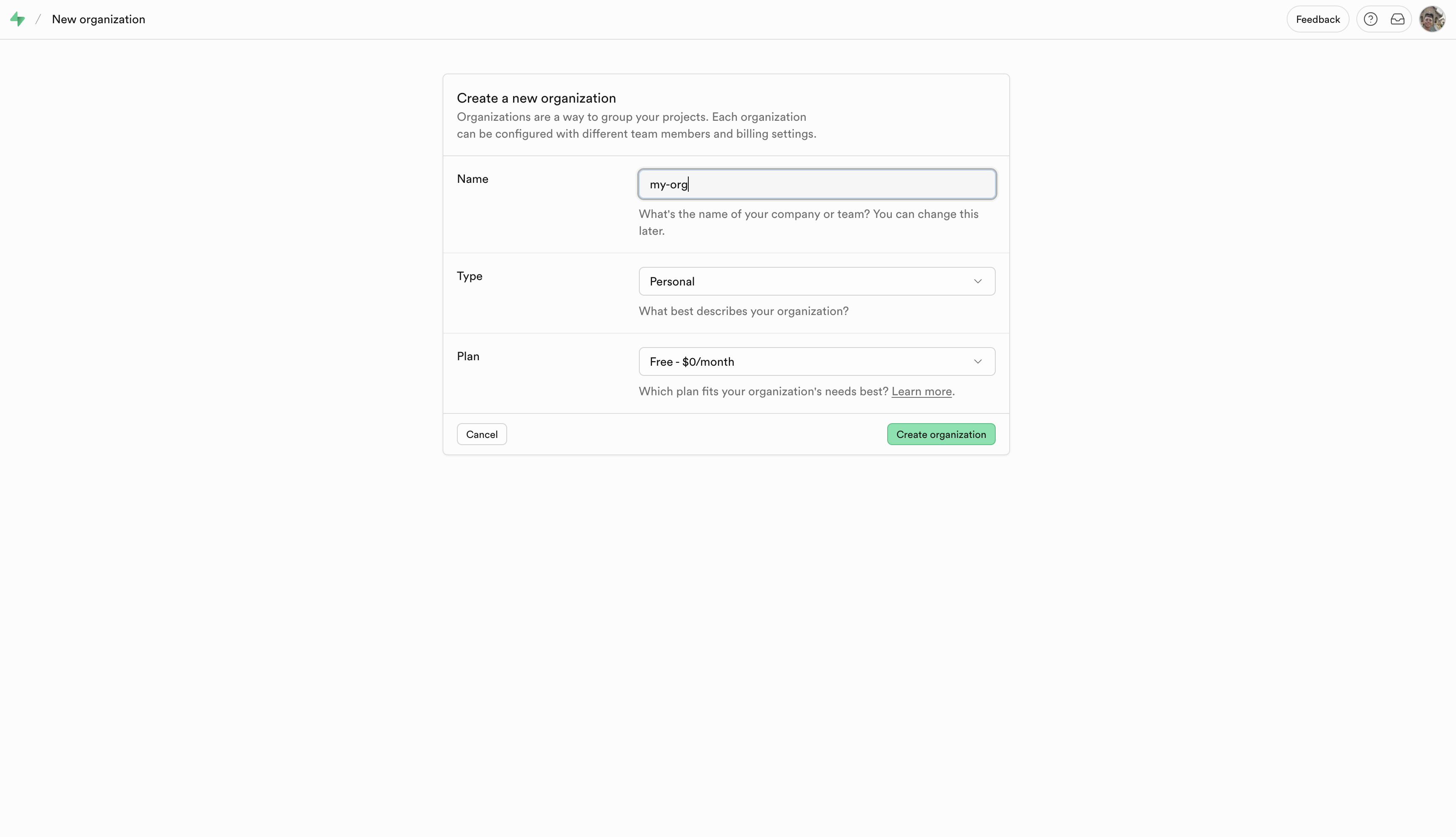
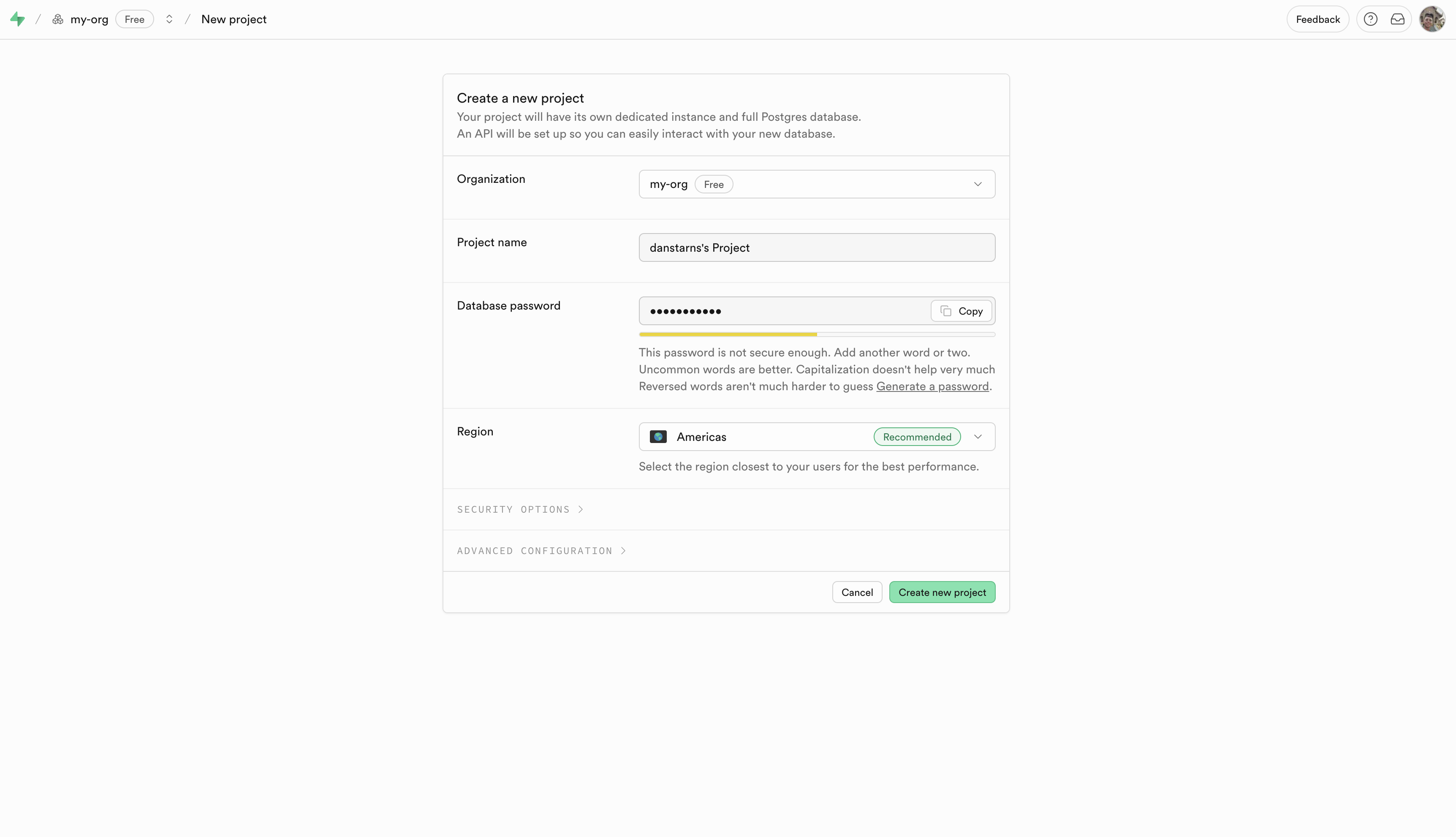
Step 2: Create an Organization and Project
- Click "New organization"
- Enter an organization name
- Choose a plan (Free tier works great)
- Click "Create organization"
Then create your project:
- Click "New project"
- Enter a Project name
- Generate a strong Database Password (save securely!)
- Select your Region
- Click "Create new project"
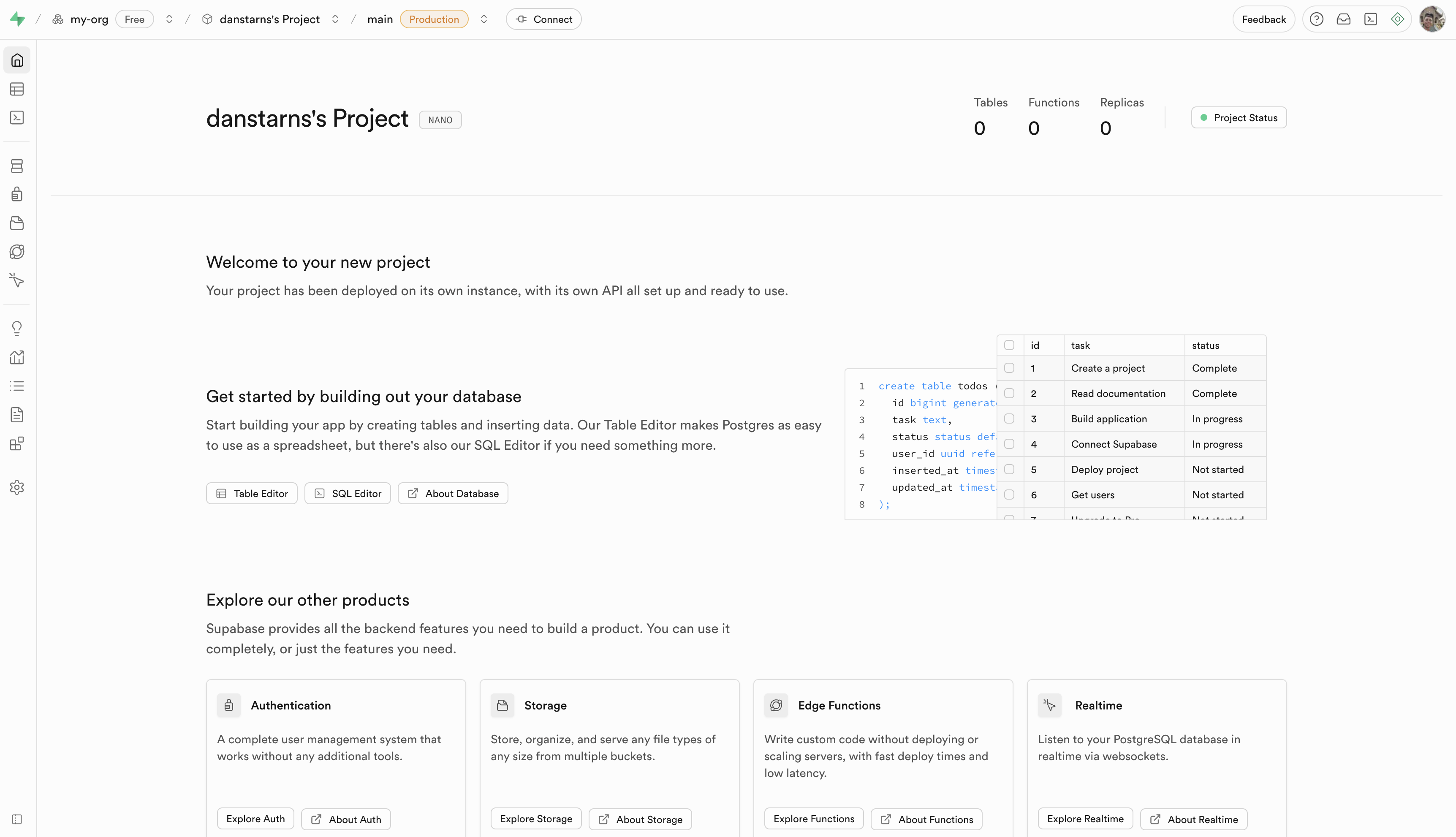
Step 3: Create Sample Data
Important: Before proceeding, you'll need to set up your database schema. Follow our comprehensive Supabase MCP Connection Guide to:
- Create the movies table using the SQL Editor
- Populate it with sample data
- Test your database setup
Once you've completed the database setup from that guide, return here to continue with the GraphQL integration.
Step 4: Get Your API Credentials
- Navigate to Settings → API
- Copy your Project URL (e.g.,
https://yourproject.supabase.co) - Copy your publishable key (labeled as "anon public" in the dashboard)
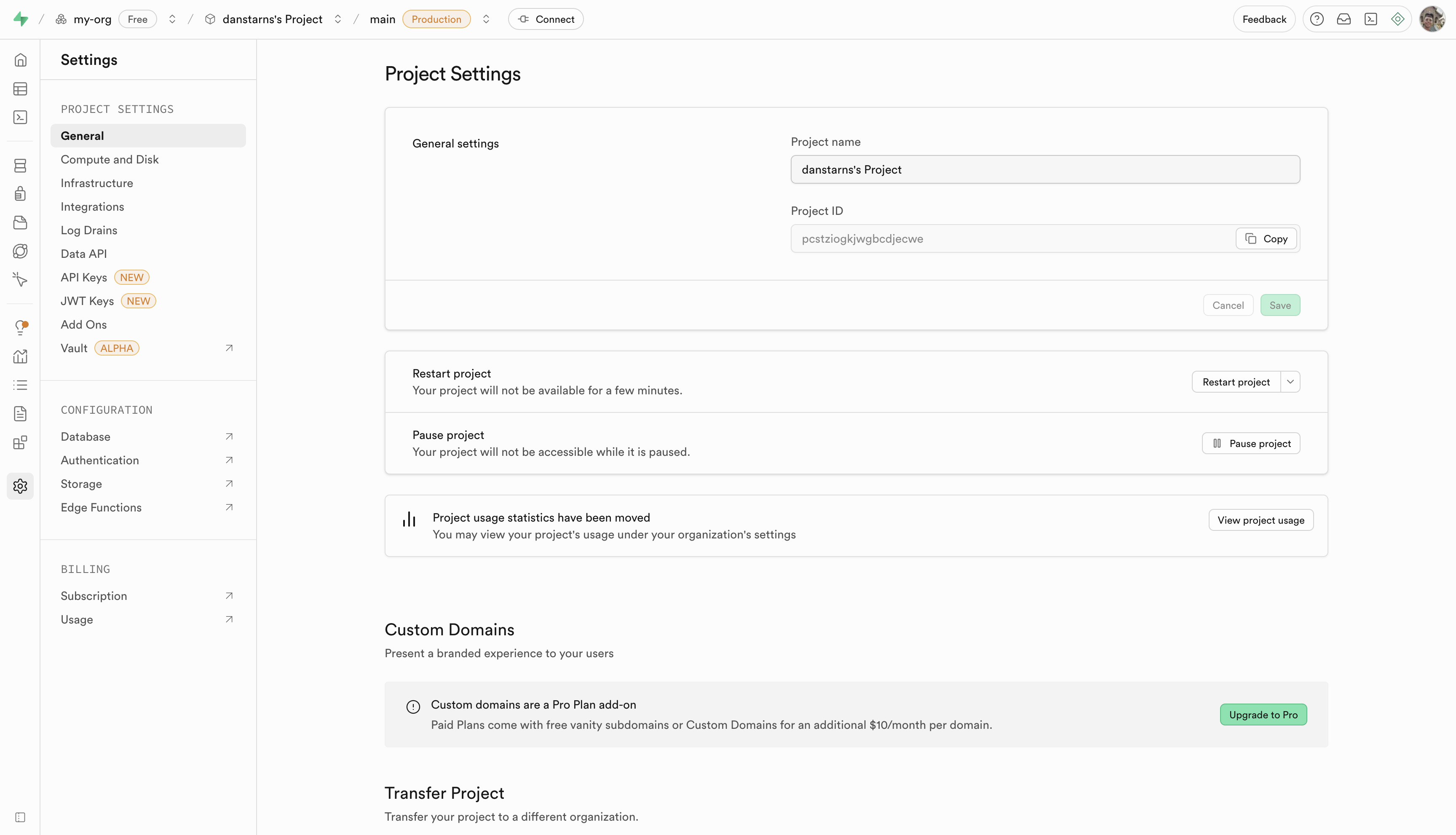
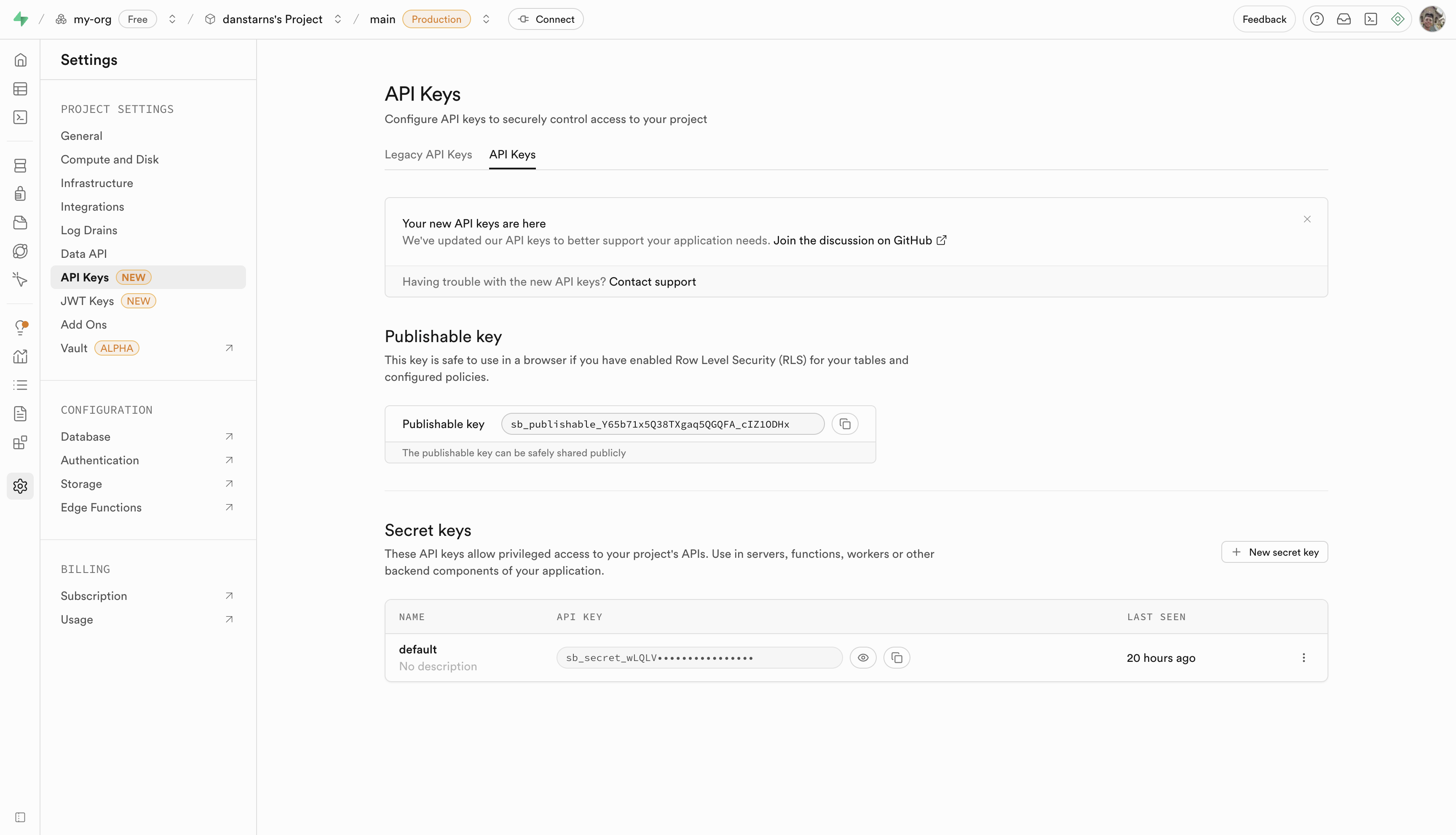
Important: Save both values - you'll need them for GraphQL authentication.
Part 2: Understanding Supabase GraphQL
Supabase automatically provides a GraphQL API for all your database tables. Here's what you need to know:
Your GraphQL Endpoint
Your GraphQL API is available at:
https://[your-project-ref].supabase.co/graphql/v1
For example: If your project URL is https://pcstziogkjwgbcdjecwe.supabase.co, your GraphQL endpoint is:
https://pcstziogkjwgbcdjecwe.supabase.co/graphql/v1
Authentication
Supabase GraphQL uses the apiKey header for authentication with your publishable key:
curl -X POST https://yourproject.supabase.co/graphql/v1 \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "apiKey: your-publishable-key-here" \
-d '{"query": "{ moviesCollection { edges { node { title director } } } }"}'
Testing Your GraphQL API
Before connecting to MCP, verify your GraphQL endpoint works:
curl -X POST https://pcstziogkjwgbcdjecwe.supabase.co/graphql/v1 \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "apiKey: your-publishable-key" \
-d '{
"query": "{ moviesCollection(first: 5) { edges { node { id title director rating } } } }"
}'
You should see your movies data returned in JSON format.
Part 3: Connecting GraphQL to MCP Connect
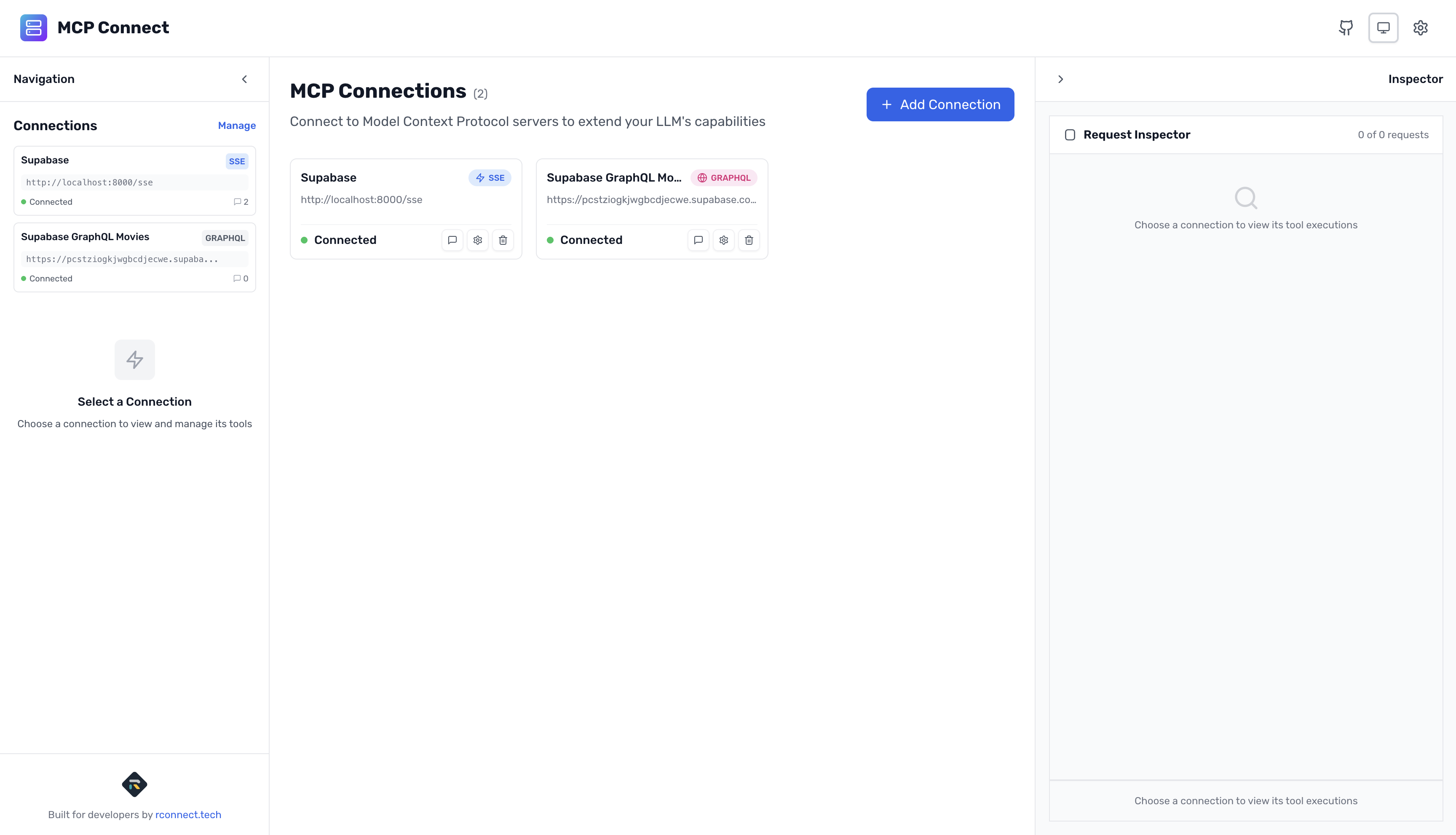
Now for the magic - we'll transform your Supabase GraphQL API into an MCP server, entirely in your browser!
Step 1: Access MCP Connect
Visit mcp.rconnect.tech - works entirely in your browser with no installation required!
Alternatively, run locally:
npx @mcpconnect/cli
Step 2: Create Your GraphQL Connection
- Click "+ New Connection" in the connections panel
- Select "GraphQL" as the connection type
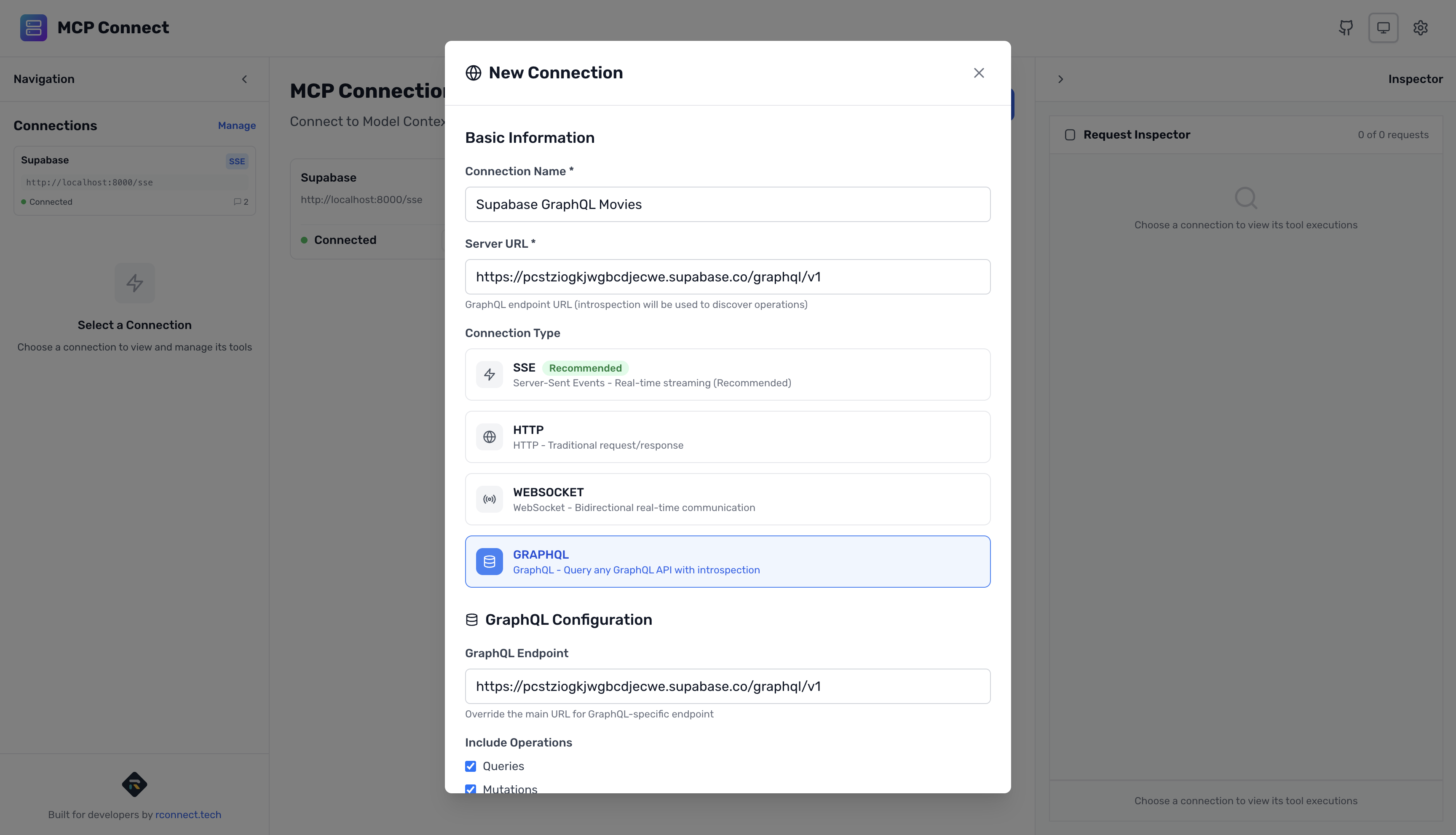
- Fill in your connection details:
Connection Configuration:
Name: Supabase GraphQL Movies
URL: https://[your-project-ref].supabase.co/graphql/v1
Connection Type: GraphQL
Authentication: API Key
Header Name: apiKey
API Key: your-publishable-key-here
Timeout: 60000ms
Retry Attempts: 3
Important Notes:
- Use your publishable key (not service role key)
- The header name must be apiKey
- Replace
[your-project-ref]with your actual project reference
- Click "Test Connection" to verify
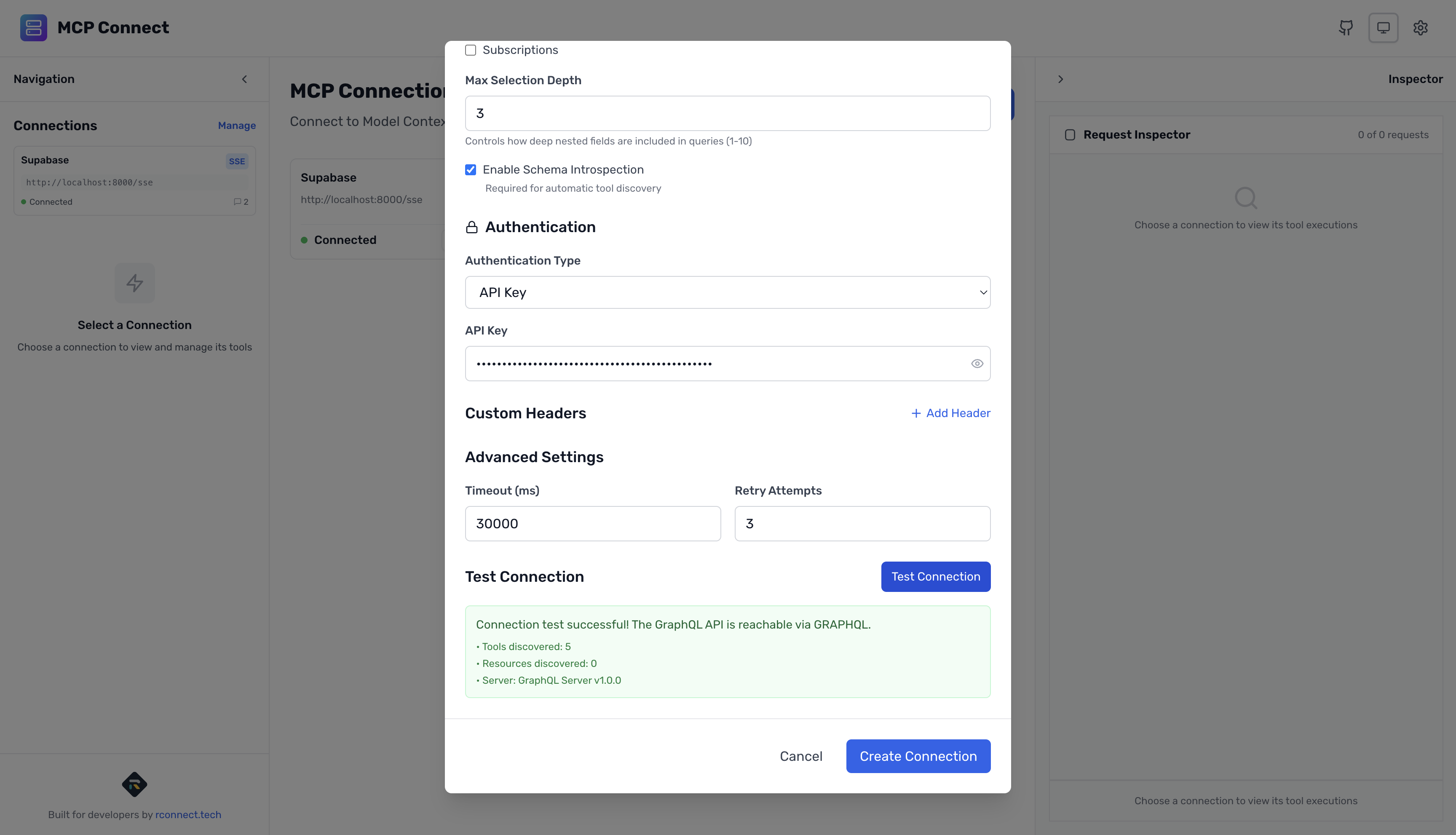
- Click "Create Connection"
What Happens During Connection
When you create a GraphQL connection, MCP Connect:
- Sends introspection query to your GraphQL endpoint
- Parses the schema to discover all available operations
- Generates MCP tools for each query and mutation
- Creates parameter definitions from GraphQL arguments
- Stores schema locally for dynamic query building
You should see:
- ✅ Connection successful
- 🔧 Tools discovered: Multiple operations converted to tools
- 📊 Server: GraphQL API
- 🌐 Endpoint: Your GraphQL URL
- 🔒 Authentication: Configured
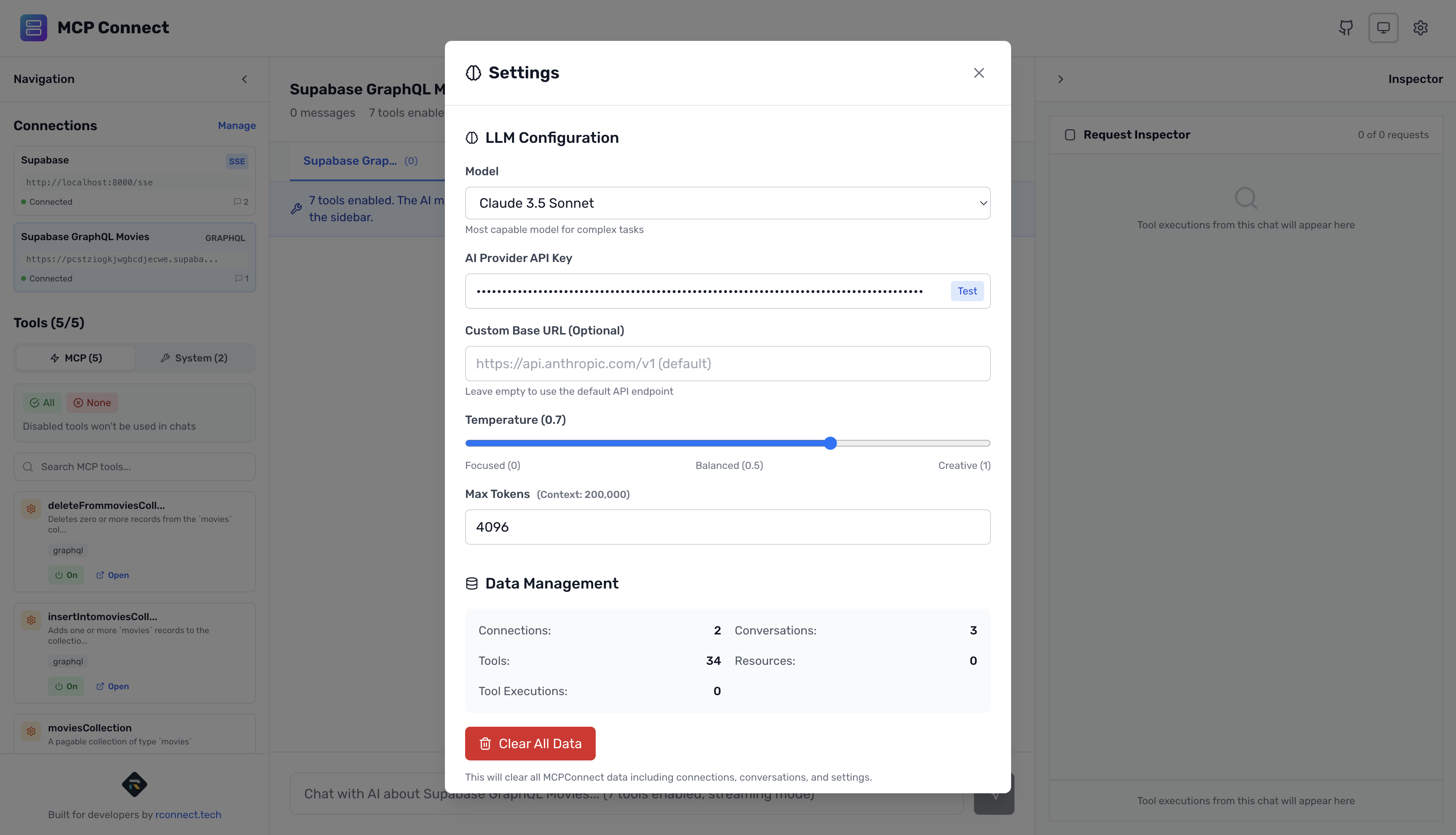
Step 3: Configure Your AI Provider
- Click the Settings icon (⚙️) in the header
- Select Anthropic as your provider
- Enter your API key from console.anthropic.com
- Choose Claude 3.5 Sonnet (recommended)
- Click Test to verify
- Click Save
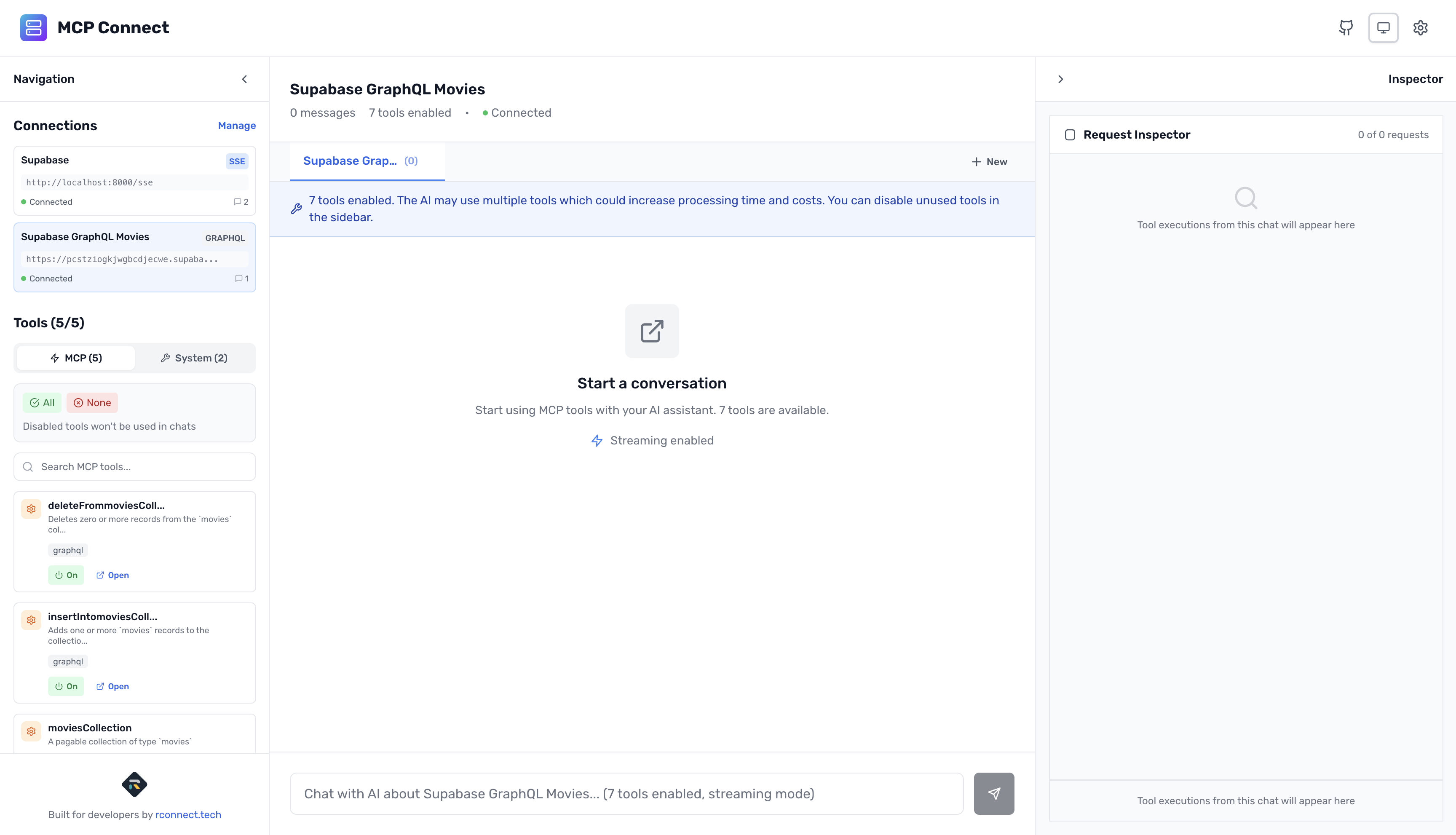
Step 4: Understanding Your GraphQL Tools
Once connected, the left sidebar shows your discovered tools organized by operation type:
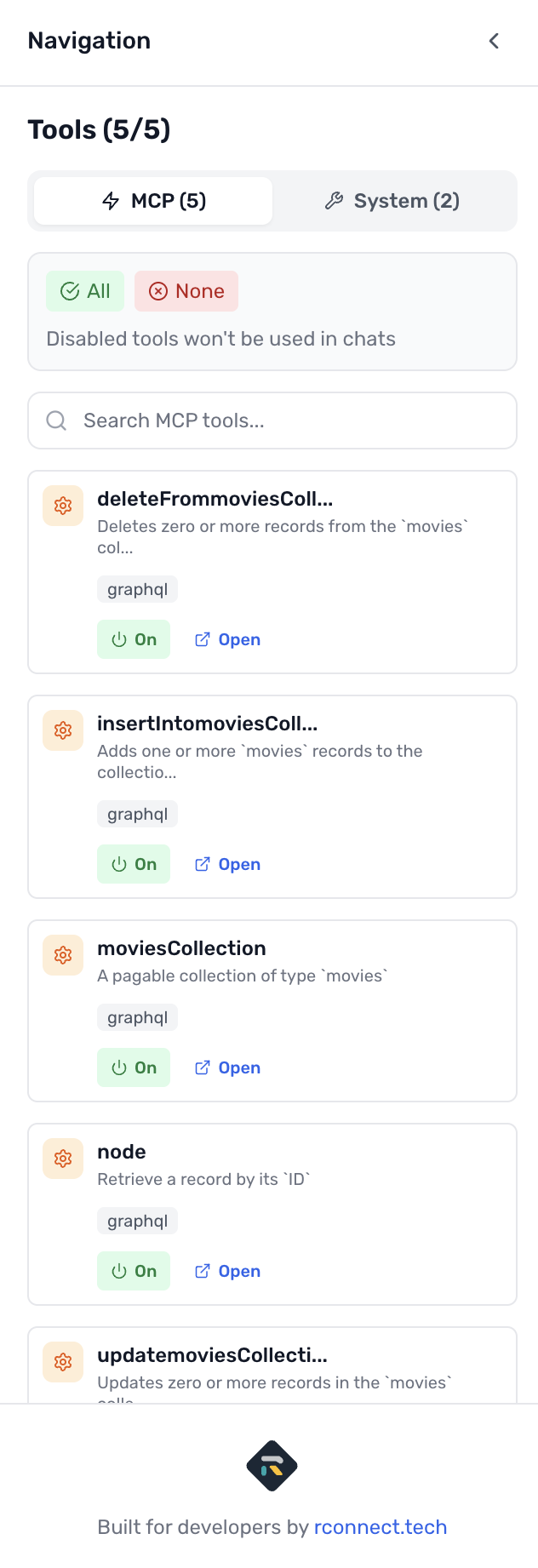
Queries (Read Operations)
moviesCollection- Query movies with filters and pagination- Each tool shows available arguments and return type
Mutations (Write Operations)
insertIntoMoviesCollection- Create new moviesupdateMoviesCollection- Update existing moviesdeleteFromMoviesCollection- Delete movies
Special _fields Parameter
Every GraphQL tool gets a special _fields parameter:
{
"_fields": {
"id": true,
"title": true,
"director": true,
"rating": true,
// AI decides which fields to include
}
}
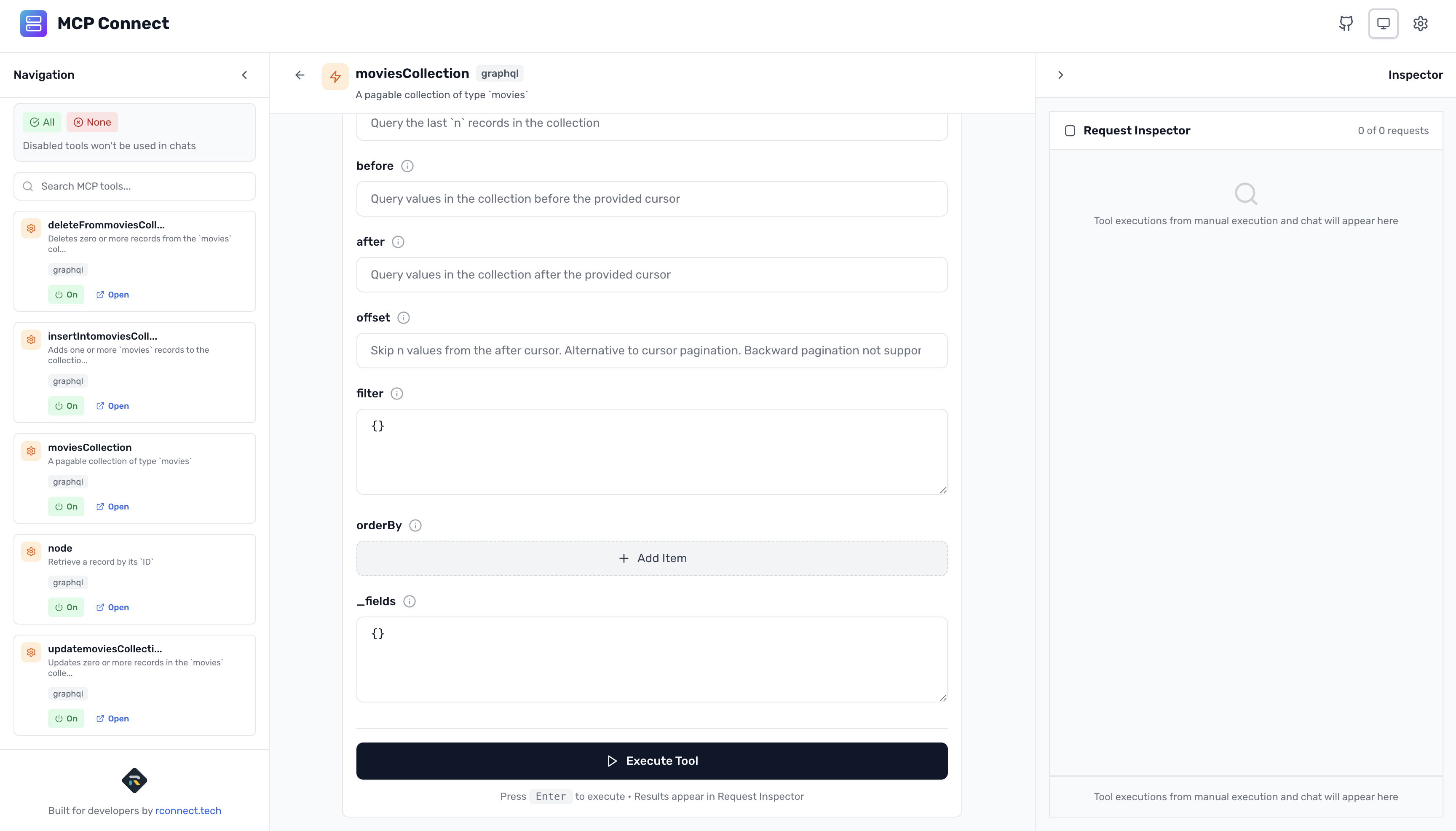
This is how the AI controls field selection without writing GraphQL queries!
Part 4: Testing Your GraphQL Integration
Now let's see the magic happen! Try these prompts:
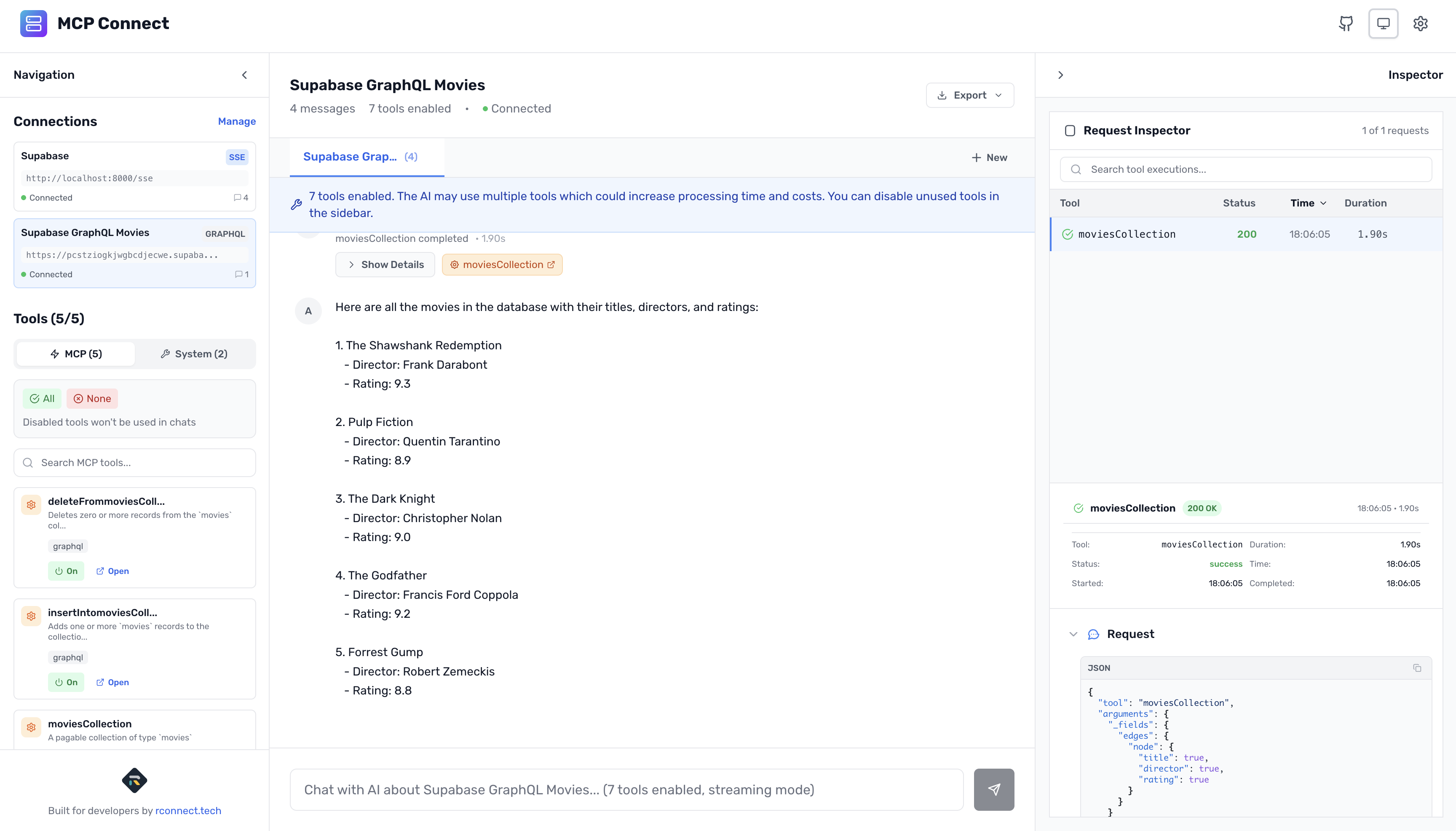
Query 1: Simple Data Retrieval
Show me all movies in the database with their titles, directors, and ratings
What happens behind the scenes:
- AI identifies it needs the
moviesCollectiontool - AI calls tool with
_fields: { title: true, director: true, rating: true } - MCP Connect builds the GraphQL query dynamically
- Query executes and returns data
- AI formats the response naturally
Query 2: Filtered Query
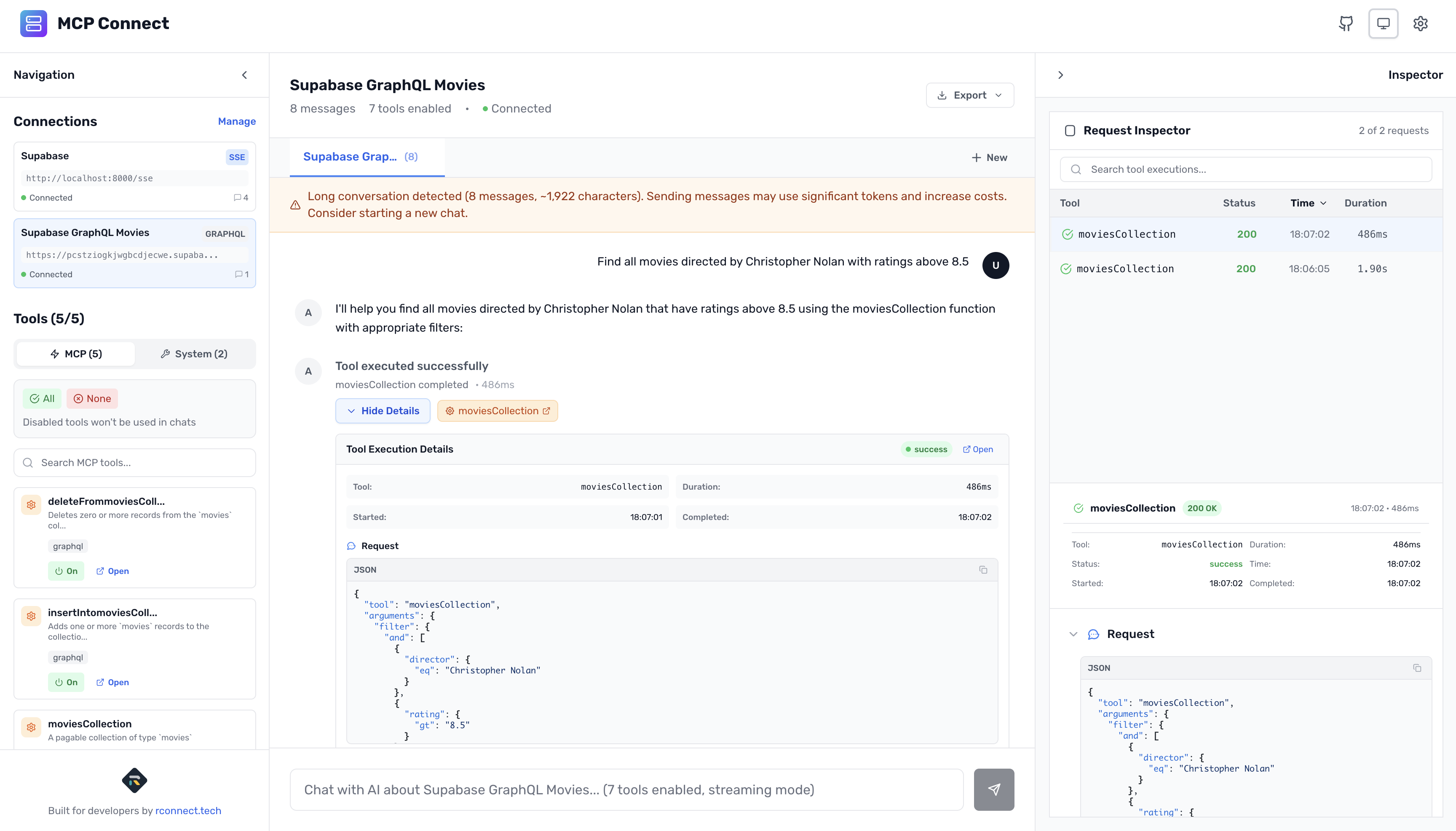
Find all movies directed by Christopher Nolan with ratings above 8.5
Behind the scenes:
{
filter: {
director: { eq: "Christopher Nolan" },
rating: { gt: 8.5 }
},
_fields: {
title: true,
release_year: true,
rating: true
}
}
Query 3: Mutation Example
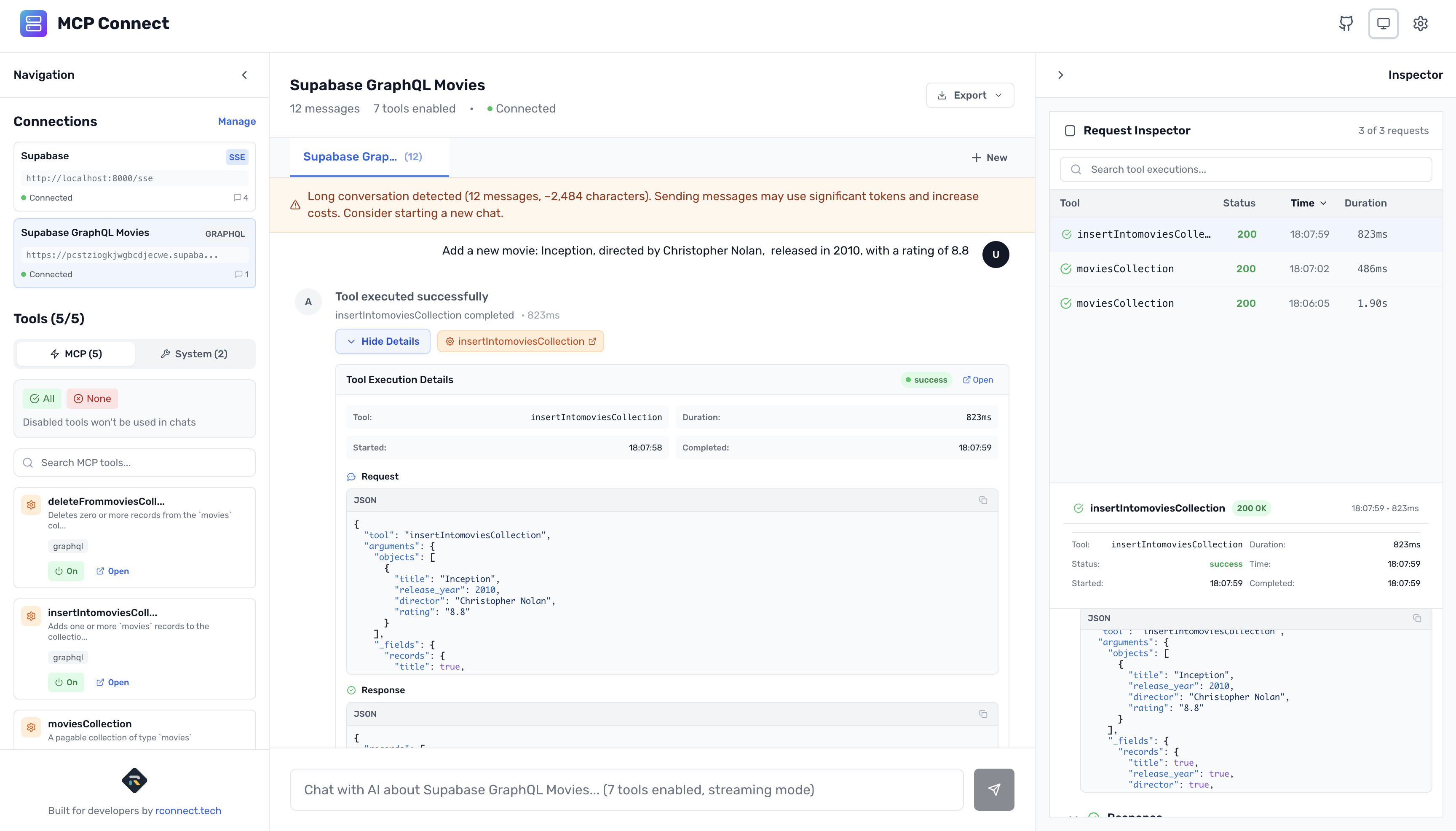
Add a new movie: Inception, directed by Christopher Nolan,
released in 2010, with a rating of 8.8
Behind the scenes:
- AI calls
insertIntoMoviesCollection - Provides object with movie data
- MCP Connect builds mutation query
- Returns created movie data
Why Direct Schema Injection Doesn't Work
Before MCP Connect, developers tried putting GraphQL schemas directly into AI prompts. Here's why that approach fails:
The Token Explosion Problem
GraphQL schemas, especially production ones, can be massive:
type Query {
moviesCollection(
first: Int
last: Int
before: Cursor
after: Cursor
filter: MoviesFilter
orderBy: [MoviesOrderBy!]
): MoviesConnection
# ... 50+ more collections ...
}
# ... hundreds more types ...
Problems with schema injection:
- Token waste: Large portion of context consumed by schema
- Context pollution: Less room for actual conversation
- Slow responses: AI must parse massive schema on every request
- Outdated schema: Copy-paste means schema goes stale
The Manual Query Construction Trap
Even worse is asking the AI to construct full GraphQL queries:
❌ BAD: "Here's my schema, write a query to get movies"
This leads to:
- AI hallucinating non-existent fields
- Missing required arguments
- Incorrect filter syntax
- No type safety or validation
The MCP Connect Solution: Dynamic Tool Generation
MCP Connect takes a completely different approach:
1. Automatic Schema Introspection
Instead of injecting schemas into prompts, MCP Connect:
- Introspects your GraphQL endpoint once during connection
- Converts each operation (query/mutation) into an MCP tool
- Stores tool definitions locally (not in AI context)
- Sends only relevant tools when AI needs them
2. AI-Controlled Field Selection
Here's the breakthrough: The AI doesn't write GraphQL queries. Instead:
- AI calls MCP tools with desired fields as parameters
- MCP Connect builds the GraphQL query dynamically
- Selection set is constructed from AI's field choices
- Query executes with precise field selection
Example flow:
// What the AI sees (simple tool call):
{
tool: "moviesCollection",
arguments: {
first: 5,
_fields: {
title: true,
director: true,
rating: true
}
}
}
// What MCP Connect generates (full GraphQL):
query moviesCollection($first: Int) {
moviesCollection(first: $first) {
edges {
node {
__typename
title
director
rating
}
}
}
}
3. Token Efficiency
Traditional approach: Thousands of tokens per request for schema MCP Connect approach: Minimal tokens for tool definitions
Significant reduction in token usage!
Essential Resources
Tools & Platforms
- MCP Connect Web - Browser-based GraphQL MCP client
- MCP Connect CLI - Local development server
- Supabase - Instant GraphQL APIs
- Supabase GraphQL Docs - Official documentation
Documentation
- GraphQL Spec - Official GraphQL documentation
- GraphQL Introspection - Schema introspection guide
- MCP Specification - Protocol details
- Supabase API Reference - Complete API guide
Connect with Us
We're passionate about connecting people through open source and building tools that make developers' lives easier. MCP Connect is part of our mission to enhance the open-source ecosystem and foster community engagement.
Get Involved:
- Try MCP Connect with your GraphQL API
- Join our YouTube community for tutorials
- Follow us on Twitter/X for updates
- Connect on LinkedIn
- Explore our open source projects
Written by the Rocket Connect team. We connect people through open source by enhancing the ecosystem and fostering community engagement. Our services include Open Source Development, Community Management, Developer Relations, and Software Training.
Ready to collaborate? Contact us today and let's build something great together!
Have a GraphQL API? Share your integration story with us—we'd love to feature your use case!